Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Nanjing Fred Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (25) 8469-6168 | |||
 |
Austin@fredchem.cn | |||
 |
Skype Chat | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: NJFred01 | |||
 |
WhatsApp: +86 17302533743 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2020 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Classification | Organic raw materials >> Carboxylic compounds and derivatives >> Carboxylic esters and their derivatives |
|---|---|
| Name | tert-butyl N-(3-acetylpyridin-2-yl)carbamate |
| Molecular Structure | 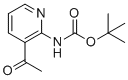 |
| Molecular Formula | C12H16N2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 236.27 |
| CAS Registry Number | 1166997-11-0 |
| SMILES | CC(=O)C1=C(N=CC=C1)NC(=O)OC(C)(C)C |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 326.0±27.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)* |
| Flash point | 151.0±23.7 ºC (Calc.)* |
| Index of refraction | 1.545 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details |
|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335 Details |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P264-P270-P271-P280-P301+P312-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P330-P332+P313-P337+P313-P362-P403+P233-P405-P501 Details |
| SDS | Available |
|
tert-Butyl N-(3-acetylpyridin-2-yl)carbamate is an organic compound composed of a substituted pyridine ring bearing an acetyl group at the 3-position and a carbamate moiety at the 2-position, where the nitrogen of the carbamate is protected by a tert-butoxycarbonyl (Boc) group. This structure integrates three functional regions: a heteroaromatic pyridine core, a ketone group contributing electrophilic reactivity, and a Boc-protected carbamate functioning as an amine surrogate that is often used in synthesis and drug design. The compound is typically encountered as a synthetic intermediate in organic and medicinal chemistry. The introduction of the tert-butyl carbamate group is a widely employed strategy for the temporary protection of amines during multistep synthesis. The Boc group is stable under mildly basic and neutral conditions, yet can be selectively removed under acidic conditions such as treatment with trifluoroacetic acid, which is advantageous for orthogonal protection strategies. The pyridine ring serves as a versatile scaffold due to its electron-deficient nature and its ability to coordinate with metal centers, making it a frequent structural component in bioactive molecules, ligands for metal catalysts, and small-molecule inhibitors. In this compound, substitution at the 2- and 3-positions allows for regioselective functionalization. The acetyl group at the 3-position adds a carbonyl functionality that can undergo further transformations, such as condensation reactions, reductions, or nucleophilic additions. tert-Butyl N-(3-acetylpyridin-2-yl)carbamate is usually synthesized through a two-step approach. The first step involves the formation of a 2-amino-3-acetylpyridine derivative, which can be obtained from the selective amination of 3-acetylpyridine or through cyclization reactions involving pyridyl precursors. The second step involves treatment of the amine with di-tert-butyl dicarbonate (Boc2O) in the presence of a base such as triethylamine or sodium carbonate. This results in the formation of the Boc-protected carbamate. In medicinal chemistry, this compound and related analogs are of interest due to their potential in lead optimization, where various substitutions on the pyridine core and at the carbamate nitrogen are investigated to enhance biological activity, metabolic stability, or bioavailability. Pyridine-containing carbamates are found in several pharmacologically active compounds, including inhibitors of kinases, proteases, and enzymes associated with neurological pathways. The acetyl group adds lipophilicity and can interact with hydrophobic pockets in protein targets, while the carbamate can act as a hydrogen bond donor or acceptor. Another area where tert-butyl N-(3-acetylpyridin-2-yl)carbamate may be utilized is in ligand development for transition metal catalysis. The nitrogen atom on the pyridine ring can coordinate to metals such as palladium, copper, or ruthenium, facilitating catalytic cycles. The presence of a carbamate group can influence the electronic and steric properties of the ligand, tuning reactivity and selectivity in catalytic processes such as cross-coupling reactions or C–H activation. This compound also serves as a valuable intermediate in fragment-based drug discovery. Its compact and functionalized nature makes it suitable for incorporation into fragment libraries designed for high-throughput screening against diverse biological targets. The ability to rapidly modify either the ketone or the Boc-protected nitrogen enhances its utility in medicinal chemistry campaigns. Overall, tert-butyl N-(3-acetylpyridin-2-yl)carbamate is a synthetically accessible and functionally rich molecule. It is primarily used in synthetic organic chemistry and drug discovery as a building block for the preparation of more complex heterocyclic and nitrogen-containing compounds, with potential applications spanning chemical biology, pharmaceutical development, and coordination chemistry. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for tert-butyl N-(3-acetylpyridin-2-yl)carbamate |