Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Nanjing Fred Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (25) 8469-6168 | |||
 |
Austin@fredchem.cn | |||
 |
Skype Chat | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: NJFred01 | |||
 |
WhatsApp: +86 17302533743 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2020 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Classification | Pharmaceutical intermediate >> Heterocyclic compound intermediate >> Pyridine compound >> Aminopyridine |
|---|---|
| Name | 3-(3-(Chloromethyl)isoxazol-5-yl)pyridin-2-amine |
| Molecular Structure | 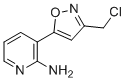 |
| Molecular Formula | C9H8ClN3O |
| Molecular Weight | 209.63 |
| CAS Registry Number | 1166997-20-1 |
| SMILES | C1=CC(=C(N=C1)N)C2=CC(=NO2)CCl |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 404.6±40.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)* |
| Flash point | 198.5±27.3 ºC (Calc.)* |
| Index of refraction | 1.609 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
|
3-(3-(Chloromethyl)isoxazol-5-yl)pyridin-2-amine is a heterocyclic compound composed of a pyridine ring substituted with an amino group at the 2-position and a 3-(chloromethyl)isoxazol-5-yl moiety at the 3-position. The compound combines two nitrogen-containing aromatic systems—pyridine and isoxazole—both of which are frequently found in medicinal chemistry due to their ability to participate in hydrogen bonding, π-π stacking, and coordination with metal centers. The isoxazole ring, a five-membered heterocycle containing one nitrogen and one oxygen atom, has been explored extensively since the early 20th century for its stability and synthetic versatility. Its inclusion in a molecule often enhances biological activity, and the 3-(chloromethyl) substituent introduces a site for further chemical modification via nucleophilic substitution. This reactive chloromethyl group allows the introduction of various substituents, such as amines, thiols, and alcohols, making the compound a valuable synthetic intermediate in the preparation of diverse analogs. The presence of the 2-aminopyridine moiety is also significant. 2-Aminopyridines are known pharmacophores in medicinal chemistry and serve as key intermediates in the synthesis of kinase inhibitors, anti-inflammatory agents, and central nervous system-active compounds. The amino group at the 2-position is nucleophilic and can be acylated, alkylated, or condensed with carbonyl-containing reagents to form Schiff bases, ureas, and other functionalized derivatives. The compound’s design suggests potential applications in drug discovery, especially as a scaffold for the development of small molecule inhibitors. Isoxazole-containing compounds have demonstrated activity across a range of biological targets, including antimicrobial, antiviral, and anticancer pathways. In particular, the isoxazole ring may mimic functional groups such as carboxylic acids or amides, allowing for bioisosteric replacement in lead optimization. The synthesis of 3-(3-(chloromethyl)isoxazol-5-yl)pyridin-2-amine typically begins with the formation of the isoxazole ring, often via a 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between a nitrile oxide and an alkyne or alkene. Alternatively, the isoxazole can be constructed from hydroxylamine and a β-ketoester or α-diketone under acidic or neutral conditions. The chloromethylation of the isoxazole ring is accomplished using chloromethylating agents such as chloromethyl methyl ether or formaldehyde with hydrochloric acid under carefully controlled conditions to avoid overchlorination or decomposition of the heterocycle. Once the isoxazole ring is constructed and functionalized, it can be coupled to the 2-aminopyridine moiety through carbon–carbon or carbon–nitrogen bond formation, often facilitated by transition metal catalysis or nucleophilic substitution strategies. The final compound is typically isolated as a solid and can be purified using chromatography techniques. Its stability under ambient conditions is generally good, though the chloromethyl group requires protection from hydrolysis and nucleophilic attack during storage. In laboratory and industrial settings, this compound is mainly used as a building block in medicinal chemistry programs, combinatorial synthesis, and library generation. Its bifunctional nature—combining a reactive halide with an amino group—allows it to participate in diverse chemical transformations, making it highly versatile for structure–activity relationship (SAR) studies. Safety handling of 3-(3-(chloromethyl)isoxazol-5-yl)pyridin-2-amine involves precautions typical of halogenated heteroaromatic compounds. The chloromethyl group can be reactive and potentially alkylating, so use of gloves and fume hoods is recommended. Disposal should follow institutional guidelines for halogenated organics. In summary, 3-(3-(chloromethyl)isoxazol-5-yl)pyridin-2-amine is a strategically designed heterocyclic compound with proven utility as a synthetic intermediate. Its structure enables modifications that support the development of new bioactive molecules, particularly in pharmaceutical research and related fields. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 3-(3-(Chloromethyl)isoxazol-5-yl)pyridin-2-amine |