Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| MolScanner | Singapore | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 18621675448 | |||
 |
marketing@molscanner.com | |||
 |
WhatsApp: 9896 7603 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2025 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Classification | Pharmaceutical intermediate >> Heterocyclic compound intermediate >> Pyrimidine compound |
|---|---|
| Name | 2-Chloro-5-(difluoromethoxy)pyrimidine |
| Molecular Structure | 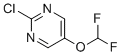 |
| Molecular Formula | C5H3ClF2N2O |
| Molecular Weight | 180.54 |
| CAS Registry Number | 1192813-64-1 |
| EC Number | 823-560-5 |
| SMILES | C1=C(C=NC(=N1)Cl)OC(F)F |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 260.1±30.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)* |
| Flash point | 111.1±24.6 ºC (Calc.)* |
| Index of refraction | 1.469 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H312-H315-H319-H332-H335 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P264-P264+P265-P270-P271-P280-P301+P317-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P317-P319-P321-P330-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P403+P233-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2-Chloro-5-(difluoromethoxy)pyrimidine is a halogenated heterocyclic compound derived from pyrimidine, bearing a chlorine atom at the 2-position and a difluoromethoxy group at the 5-position. Its molecular structure features a six-membered aromatic diazine ring, which includes two nitrogen atoms at the 1 and 3 positions, forming the backbone of numerous biologically active molecules in medicinal and agrochemical research. The substitution pattern imparts distinct electronic and steric characteristics, enhancing its reactivity and functional versatility in synthetic chemistry. The synthesis and development of substituted pyrimidines such as 2-chloro-5-(difluoromethoxy)pyrimidine emerged from the broader study of nitrogen-containing heterocycles, a core area of interest in pharmaceutical and agrochemical discovery. Halogenated pyrimidines are particularly valued for their role as key intermediates in cross-coupling reactions, nucleophilic substitution, and heterocyclic ring functionalization. The presence of the chlorine atom in the 2-position facilitates such transformations through its ability to serve as a leaving group in reactions catalyzed by transition metals or under basic conditions. Simultaneously, the difluoromethoxy moiety at the 5-position contributes unique electronic properties that affect the compound's polarity and reactivity. This compound has been used as a precursor or intermediate in the synthesis of more complex molecules, particularly those targeting biological systems such as enzymes, receptors, or nucleic acid-related processes. The difluoromethoxy group is a bioisosteric replacement for hydroxyl or methoxy groups in medicinal chemistry, often used to fine-tune the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of candidate compounds. Its electron-withdrawing nature can alter hydrogen bonding capacity and increase lipophilicity, potentially improving membrane permeability and metabolic stability. In medicinal chemistry, derivatives of 2-chloro-5-(difluoromethoxy)pyrimidine have been incorporated into structures exhibiting antiviral, antibacterial, and anticancer activities. The pyrimidine scaffold itself is a common structural motif in DNA and RNA bases, and synthetic analogs are frequently designed to interfere with nucleotide processing enzymes, such as kinases or polymerases. Substituted pyrimidines also appear in kinase inhibitors, where specific patterns of substitution influence binding to ATP-binding pockets. The compound’s synthesis typically involves selective halogenation and subsequent alkylation of appropriately substituted pyrimidine precursors. The introduction of the difluoromethoxy group is achieved through the use of difluorocarbene reagents or difluoromethyl ethers under suitable reaction conditions. The resulting material is usually purified by recrystallization or chromatographic techniques to afford the compound in high purity suitable for further derivatization. 2-Chloro-5-(difluoromethoxy)pyrimidine’s role as a functionalized intermediate makes it attractive for libraries of small molecules in high-throughput screening applications. Its dual reactivity—through the electrophilic 2-chloropyrimidine site and the electron-rich difluoromethoxy substituent—offers multiple points of synthetic elaboration, enabling the construction of structurally diverse analogs with potential biological activity. In agrochemistry, compounds derived from halogenated pyrimidines have been used in the development of herbicides and fungicides. Their selective bioactivity and favorable environmental stability are often attributed to the properties imparted by fluorinated substituents, which can resist biodegradation and enhance systemic action in plant tissues. Because of its established reactivity and structural features, 2-chloro-5-(difluoromethoxy)pyrimidine remains a valuable synthetic intermediate in both pharmaceutical and agrochemical research programs. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 2-Chloro-5-(difluoromethoxy)pyrimidine |