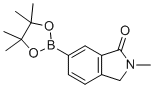
The chemical substance 2-methyl-6-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-isoindol-1-one, commonly referred to as a Boc-protected isoindolinone with a pinacol boronate group, is a functionalized heterocyclic compound widely used as a synthetic intermediate in pharmaceutical and materials chemistry. Its discovery and applications are well-documented in the literature, rooted in the development of isoindolinone derivatives and organoboron chemistry.
The origins of this compound are tied to the study of isoindolinones, bicyclic heterocycles comprising a benzene ring fused to a five-membered lactam, which have been explored since the early 20th century for their presence in natural products and pharmacological activity. The 2,3-dihydro-1H-isoindol-1-one core, a partially saturated isoindolinone, gained attention in the mid-20th century for its stability and versatility in medicinal chemistry. The introduction of a boronic ester, specifically the 4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl (pinacol boronate) group, became prominent in the 1980s and 1990s with the advent of Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reactions, pioneered by Akira Suzuki. The N-methylation at the 2-position and the boronic ester at the 6-position emerged in the late 20th century, driven by the pharmaceutical industry’s need for reactive, functionalized heterocycles to construct complex drug molecules.
Synthetically, 2-methyl-6-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-isoindol-1-one is prepared through a multi-step process. A typical route starts with 6-bromo-2-methyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-isoindol-1-one, synthesized by cyclizing a 2-bromobenzamide derivative with methylamine or by N-methylation of an isoindolinone precursor. The bromine at the 6-position is converted to a boronic ester via palladium-catalyzed borylation with bis(pinacolato)diboron or pinacolborane, using a base and a phosphine ligand to facilitate the reaction. Alternatively, the isoindolinone core can be constructed from a phthalimide precursor, reduced to the dihydro form, and then functionalized with the boronic ester. These steps rely on well-established heterocyclic synthesis and organoboron chemistry protocols, ensuring regioselectivity and high yields.
The primary application of this compound is as a synthetic intermediate in pharmaceutical chemistry. The isoindolinone core is a privileged scaffold in drugs targeting cancer, neurological disorders, and inflammation, due to its rigid structure and ability to engage in hydrogen bonding. The 6-(pinacol boronate) group serves as a handle for Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reactions, enabling the introduction of aryl, alkenyl, or alkynyl groups to the aromatic ring. The N-methyl group at the 2-position modulates steric and electronic properties, enhancing binding affinity, while the lactam provides a site for further functionalization. This compound is frequently used in the synthesis of kinase inhibitors, receptor modulators, and analgesic agents, where the combination of the heterocyclic core and boronic ester optimizes pharmacokinetic properties and target specificity.
In addition to pharmaceuticals, the compound is employed in materials science for synthesizing functionalized polymers or ligands, where the boronic ester facilitates cross-coupling to build complex molecular architectures. In academic research, it serves as a model compound for studying cross-coupling mechanisms, isoindolinone reactivity, and the effects of N-methylation on heterocyclic properties. Its synthesis has contributed to the development of new borylation methods and catalysts.
The significance of 2-methyl-6-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-isoindol-1-one lies in its role as a multifunctional intermediate that combines the biological relevance of isoindolinones with the synthetic versatility of boronic esters. Its development reflects progress in heterocyclic functionalization and organoboron chemistry. By enabling the efficient synthesis of complex, biologically active molecules, it has become a critical tool in advancing pharmaceutical, materials, and chemical research.
|



 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details