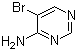
4‑Amino‑5‑bromopyrimidine (CAS 1439‑10‑7) is a heterocyclic organic compound with the molecular formula C₄H₄BrN₃ and a molecular weight of about 174.00 g/mol. The pyrimidine ring is substituted at the 4‑position by an amino group and at the 5‑position by a bromine atom. This structure gives it both nucleophilic and electrophilic character, making it a useful building block in synthetic chemistry.
The compound is commercially available, typically with ≥ 98 % purity. It is slightly soluble in water, according to catalog specifications from chemical suppliers. Because of its bromine substituent, it is reactive to cross-coupling chemistries (e.g., Suzuki or Buchwald-type couplings) and also to nucleophilic substitution, enabling the introduction of various substituents onto the pyrimidine ring.
One of the notable reported activities is its role as an inhibitor of thymidine phosphorylase, an enzyme that is overexpressed in some types of tumors and linked to cancer metastasis. This makes 4‑amino-5‑bromopyrimidine of interest in medicinal chemistry research, particularly for developing anticancer agents.
In the lab, the compound can serve as a versatile intermediate for further functionalization. The amino group at position 4 enables derivatization through acylation, reductive amination, or coupling reactions, while the bromo group at position 5 can be replaced or extended to form more complex heterocyclic compounds. Its pyrimidine core provides a stable heterocyclic scaffold often used in drug discovery and in the synthesis of nucleoside analogs.
Because it is used as an intermediate rather than an active pharmaceutical ingredient itself, detailed pharmacological studies are more limited; most of the information on this compound comes from supplier data or its use in synthetic pathways. Handling typically involves standard precautions for brominated heterocycles, including use of dry solvents and inert atmosphere to avoid unwanted side reactions.
|






 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details