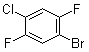
1-Bromo-4-chloro-2,5-difluorobenzene is an organic compound belonging to the class of halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons. It features a benzene ring substituted with bromine, chlorine, and two fluorine atoms at specific positions. The structure consists of a bromine atom at position 1, a chlorine atom at position 4, and fluorine atoms at positions 2 and 5 on the benzene ring. This combination of halogen atoms significantly influences the chemical reactivity and physical properties of the compound, making it a useful intermediate in organic synthesis.
The discovery of 1-bromo-4-chloro-2,5-difluorobenzene is part of the broader interest in halogenated aromatic compounds, which are widely studied for their electronic properties and reactivity. The incorporation of fluorine atoms in particular plays a key role in altering the electronic structure of the molecule, enhancing its stability, and influencing its reactivity in chemical reactions. The fluorine atoms are highly electronegative, which results in a significant electron-withdrawing effect, impacting the compound's ability to participate in various types of chemical reactions.
In synthetic organic chemistry, 1-bromo-4-chloro-2,5-difluorobenzene serves as a valuable building block for the preparation of more complex molecules. It is commonly used as a precursor in cross-coupling reactions such as Suzuki, Heck, and Sonogashira reactions, where the halogen atoms serve as important points of attachment for various nucleophiles or other electrophilic species. These reactions are essential for the construction of complex molecular structures that are found in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and advanced materials.
The halogen substituents in 1-bromo-4-chloro-2,5-difluorobenzene also make it useful in the development of new organic materials. Fluorine and chlorine are often incorporated into materials to modify their electronic, optical, and thermal properties. In particular, the presence of fluorine can improve the thermal stability and chemical resistance of the resulting materials, which is particularly valuable in high-performance applications such as electronic devices, sensors, and coatings.
In the pharmaceutical industry, 1-bromo-4-chloro-2,5-difluorobenzene can be used as a key intermediate in the synthesis of bioactive molecules. The halogenated benzene core is a common structural motif in many drugs, as the halogens can affect the molecule’s binding affinity, metabolic stability, and pharmacokinetics. As such, compounds containing similar halogenated benzene structures are often explored for their potential therapeutic properties, including anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and anticancer activities.
Additionally, 1-bromo-4-chloro-2,5-difluorobenzene has applications in the field of agrochemicals. Its unique combination of halogen substituents can be used to design new herbicides, insecticides, and fungicides with enhanced potency and selectivity. The fluorine atoms, in particular, are known to improve the bioavailability of agrochemicals, making them more effective in controlling pests or weeds.
In summary, 1-bromo-4-chloro-2,5-difluorobenzene is a versatile and important compound in synthetic chemistry. Its halogenated structure makes it useful in a range of applications, from pharmaceuticals to materials science and agrochemicals. The compound’s role as an intermediate in chemical reactions and its ability to modify the properties of other molecules make it an essential building block in the development of new chemical entities with potential industrial and therapeutic applications.
|

















 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details