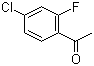
4'-Chloro-2'-fluoroacetophenone is an organic compound that consists of a benzene ring with a carbonyl group attached to an acetophenone structure, along with two halogen substituents: a chlorine atom at position 4' and a fluorine atom at position 2' on the aromatic ring. This particular combination of halogen atoms at different positions on the aromatic ring significantly influences the chemical reactivity and physical properties of the compound.
The compound was first introduced as part of studies related to the synthesis and functionalization of halogenated acetophenones, which are widely utilized as intermediates in organic synthesis. Halogenated acetophenones are known for their reactivity in a variety of chemical reactions, such as nucleophilic substitution, reduction, and electrophilic aromatic substitution. In particular, the introduction of a fluorine atom and a chlorine atom in the para and ortho positions of the aromatic ring, respectively, plays a crucial role in modulating the electron density on the ring and thereby altering the reactivity and selectivity of the compound in different reactions.
4'-Chloro-2'-fluoroacetophenone is a useful intermediate in the synthesis of various organic compounds, including pharmaceutical and agrochemical agents. The fluorine atom enhances the compound's stability, solubility, and bioavailability, while the chlorine atom further modulates the compound's electronic properties, making it a versatile building block for more complex molecules. The combination of fluorine and chlorine atoms in a single molecule can also improve the compound's physical properties, such as its thermal stability, which is important in various industrial applications.
In medicinal chemistry, 4'-chloro-2'-fluoroacetophenone and its derivatives are explored for their potential biological activities. The halogenated acetophenone core is a common structural motif found in many bioactive molecules. The unique electron-withdrawing effects of the fluorine and chlorine atoms can affect the compound’s interaction with biological targets, influencing factors such as binding affinity, metabolic stability, and pharmacokinetics. As a result, halogenated acetophenones are often investigated for their potential as anticancer, antimicrobial, or anti-inflammatory agents.
The compound's reactivity also makes it useful in the preparation of other functionalized aromatic compounds. For example, 4'-chloro-2'-fluoroacetophenone can be employed in various cross-coupling reactions, such as the Suzuki and Heck reactions, where it acts as a coupling partner to form carbon-carbon bonds. These reactions are essential for the synthesis of complex molecules used in the development of new materials, electronics, and pharmaceuticals.
In the field of agrochemicals, 4'-chloro-2'-fluoroacetophenone can be used as a starting material for the synthesis of herbicides, insecticides, and fungicides. The presence of halogen atoms enhances the compound's bioactivity and stability in environmental conditions, making it an attractive candidate for designing more effective agrochemical agents. The fluorine atom in particular contributes to the compound's lipophilicity, which is beneficial for its ability to penetrate biological membranes and exhibit increased efficacy in controlling pests or plant diseases.
In conclusion, 4'-chloro-2'-fluoroacetophenone is a versatile and valuable compound in organic synthesis. Its halogenated structure, which includes both chlorine and fluorine atoms, makes it an important intermediate for a wide range of chemical reactions. Its applications span across medicinal chemistry, agrochemicals, and materials science, where it serves as a building block for the development of novel molecules with potential therapeutic and industrial uses.
|

























 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details