Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Capot Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8558-6718 +86 13336195806 | |||
 |
capotchem@gmail.com sales@capotchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2006 | ||||
| Tyger Scientific Inc. | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (609) 434-0144 | |||
 |
sales@tygersci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1992 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| Win-Win Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (577) 6449-8589 +86 15325081899 | |||
 |
sales@win-winchemical.com winwinchemical@gmail.com | |||
 |
Skype Chat | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2007 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2011 | ||||
| Hangzhou Mole's Science&Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 5688-0228 | |||
 |
amy@mole-scitech.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2011 | ||||
| Aromsyn Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8558-5865 +86 13336024896 | |||
 |
service@aromsyn.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2012 | ||||
| Hangzhou Leap Chem Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8771-1850 | |||
 |
market19@leapchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2006 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Shanghai Edu Chemical Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 19301251526 | |||
 |
sales1@chemido.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2011 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Anvia Chemicals, LLC | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (414) 534-7845 | |||
 |
sales@anviachem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| Classification | Chemical reagent >> Organic reagent >> Aromatic acid |
|---|---|
| Name | Mono-methyl isophthalate |
| Synonyms | Isophthalic acid methyl ester |
| Molecular Structure | 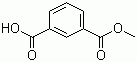 |
| Molecular Formula | C9H8O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 180.16 |
| CAS Registry Number | 1877-71-0 |
| EC Number | 619-855-1 |
| SMILES | COC(=O)C1=CC=CC(=C1)C(=O)O |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Melting point | 194 - 196 ºC (Expl.) |
| Boiling point | 339.3±25.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)* |
| Flash point | 139.6±16.7 ºC (Calc.)* |
| Index of refraction | 1.556 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P264-P264+P265-P271-P280-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P319-P321-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P403+P233-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Mono-methyl isophthalate is an aromatic dicarboxylic acid derivative in which one of the carboxylic acid groups of isophthalic acid is esterified as a methyl ester, leaving the other carboxyl group free. Its molecular formula is C9H8O4, with a molecular weight of approximately 180.16 g/mol. The compound contains a benzene ring substituted at the 1 and 3 positions with a carboxylic acid and a methyl ester, respectively, giving it a rigid planar structure and both hydrophilic and moderately lipophilic character. The compound is typically synthesized by selective esterification of isophthalic acid. Protection and deprotection strategies or controlled reaction conditions are used to ensure that only one of the two carboxylic acid groups is converted to the methyl ester. Methods often involve reacting isophthalic acid with methanol in the presence of acid catalysts under carefully monitored conditions, limiting conversion to the mono-ester. Alternative strategies include starting from substituted intermediates or using orthogonal protecting groups to achieve regioselective esterification. Chemically, mono-methyl isophthalate possesses reactivity at both the free carboxyl group and the ester. The free carboxylic acid can participate in condensation reactions, forming amides, esters, or anhydrides, while the methyl ester is stable under mild reaction conditions but can be hydrolyzed to the acid under acidic or basic conditions. This dual functionality makes the molecule versatile in organic synthesis and polymer chemistry, as it can serve both as a building block for chain elongation and as a site for selective modification. In materials science, mono-methyl isophthalate is employed in the preparation of polyesters and copolymers. The presence of one free carboxylic acid and one ester group allows for controlled polymerization reactions, enabling the introduction of functional groups at specific positions in the polymer backbone. It is used in the synthesis of functionalized polyesters for applications such as biodegradable materials, coatings, or drug delivery systems, where partial esterification can influence solubility, crystallinity, and degradation rates. In medicinal chemistry, mono-methyl isophthalate can serve as a precursor for the synthesis of biologically active molecules. The free carboxyl group can be coupled to amines to form amide bonds, creating molecules with potential pharmacological properties, while the ester group may be retained or modified depending on the desired solubility or metabolic stability. Its rigid aromatic structure provides spatial orientation useful for binding interactions in enzyme active sites or receptor pockets. The compound is generally a solid at room temperature, with moderate solubility in polar organic solvents such as ethanol, acetone, or dimethylformamide, and limited solubility in water. It is stable under ambient conditions but should be protected from strong acids or bases that could hydrolyze the ester or degrade the aromatic system. Handling precautions include using gloves and avoiding inhalation of dust to prevent irritation. Mono-methyl isophthalate’s combination of an aromatic core, a free carboxyl group, and a methyl ester allows it to function as a flexible intermediate in synthetic chemistry. Its selective reactivity and ability to be further transformed make it a useful building block for both polymer and small-molecule synthesis, where regioselective functionalization and controlled chemical modifications are required. References 2006. Rh-Catalyzed Carboxylation of Boronic Esters with CO2. Synfacts. DOI: 10.1055/s-2006-949309 2010. Direct Carboxylation of Aryl Bromides with CO2. Synfacts. DOI: 10.1055/s-0029-1219070 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Mono-methyl isophthalate |