Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Suzhou Biosyntech Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13921151340 +86 (512) 6300-1269 | |||
 |
sales2@biosyntech-suzhou.com sales@biosyntech-suzhou.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2019 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2020 | ||||
| Classification | Pharmaceutical intermediate >> Heterocyclic compound intermediate >> Pyrimidine compound |
|---|---|
| Name | (2S,3R)-3-(5-Methylpyrimidin-2-yl)butane-2-sulfonamide |
| Molecular Structure | 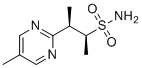 |
| Molecular Formula | C9H15N3O2S |
| Molecular Weight | 229.30 |
| CAS Registry Number | 2050017-52-0 |
| SMILES | CC1=CN=C(N=C1)[C@@H](C)[C@H](C)S(=O)(=O)N |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 375.9±44.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)* |
| Flash point | 181.2±28.4 ºC (Calc.)* |
| Index of refraction | 1.542 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details |
|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335 Details |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P264-P270-P271-P280-P301+P312-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P330-P332+P313-P337+P313-P362-P403+P233-P405-P501 Details |
| SDS | Available |
|
(2S,3R)-3-(5-Methylpyrimidin-2-yl)butane-2-sulfonamide is a small chiral organic molecule comprising a sulfonamide group and a substituted pyrimidine ring, commonly encountered in medicinal chemistry due to its structural features that support both target specificity and functional versatility. The compound’s architecture suggests potential use as a pharmacophore or a bioactive scaffold, particularly in the design of enzyme inhibitors or receptor ligands. The core structure features a butane-2-sulfonamide backbone with two chiral centers at the 2 and 3 positions, giving rise to the (2S,3R) stereochemistry. Chirality plays a crucial role in determining the biological activity and interaction of small molecules with proteins or nucleic acids. Enantiomeric specificity can significantly affect binding affinity, metabolic stability, and overall pharmacokinetic properties. At the 2-position of the butane chain is the sulfonamide functional group, –SO2NH2. Sulfonamides are known for their hydrogen bonding capabilities, often acting as bioisosteres for carboxylic acids or amides in drug design. They are also frequently present in a variety of biologically active molecules, including antibacterial agents, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, and certain classes of anti-inflammatory and antiglaucoma drugs. The sulfonamide group can interact with enzymatic active sites or protein binding pockets through a combination of hydrogen bonding and ionic interactions. Attached at the 3-position is a 5-methylpyrimidin-2-yl group, a heteroaromatic ring system commonly found in nucleic acid bases such as cytosine and thymine. The pyrimidine ring provides electron-deficient aromaticity and contains nitrogen atoms capable of hydrogen bonding and coordination to metal ions. The presence of a methyl substituent at the 5-position enhances the lipophilicity of the molecule, potentially improving membrane permeability and modulating the electronic properties of the ring. Pyrimidine derivatives are ubiquitous in medicinal chemistry due to their capacity to mimic purine and pyrimidine bases in nucleic acids. This mimicry allows pyrimidine-containing compounds to interact with DNA and RNA, or to serve as inhibitors of nucleotide-processing enzymes such as kinases, polymerases, and dehydrogenases. The substitution pattern and orientation of the ring in this compound suggest it could interact selectively with biological macromolecules, possibly through stacking interactions or via its basic nitrogen atoms forming key polar contacts. The stereochemistry of the (2S,3R) configuration introduces a defined three-dimensional shape that is critical for specific molecular recognition in biochemical systems. This configuration dictates the spatial arrangement of the sulfonamide and pyrimidine groups, which can dramatically affect how the molecule binds to enzymes, receptors, or other proteins. In rational drug design, maintaining or altering this stereochemistry can fine-tune the molecule’s activity and selectivity. Synthetically, compounds of this type can be constructed using asymmetric synthesis strategies or by resolution of racemic mixtures. Key transformations might include stereoselective alkylation, sulfonylation, and coupling with heteroaryl groups. The availability of chiral centers also allows for further derivatization into analog series for structure-activity relationship exploration. Given its combination of a biologically relevant heterocycle and a sulfonamide group, (2S,3R)-3-(5-methylpyrimidin-2-yl)butane-2-sulfonamide likely serves as a precursor or lead compound in the development of pharmaceuticals targeting metabolic enzymes, microbial pathogens, or signaling proteins. Its structural motifs are consistent with inhibitors of dihydropteroate synthase, kinases, or proteases, although exact biological applications would depend on empirical data regarding its binding properties and cellular effects. The compound’s modular structure also makes it a promising candidate for fragment-based drug discovery approaches. References 2020. Building Complexity and Achieving Selectivity through Catalysis � Case Studies from the Pharmaceutical Pipeline. Synlett, 31(15). DOI: 10.1055/s-0040-1706869 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for (2S,3R)-3-(5-Methylpyrimidin-2-yl)butane-2-sulfonamide |