Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Topscience Co. Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (400) 820-0310 | |||
 |
sales@tsbiochem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2013 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2012 | ||||
| Classification | Pharmaceutical intermediate >> Heterocyclic compound intermediate >> Pyrimidine compound >> Carboxylic acid |
|---|---|
| Name | 2,4-dichloro-5-methyl-7H-pyrrolo(2,3-d)pyrimidine-6-carboxylic acid |
| Molecular Structure | 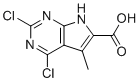 |
| Molecular Formula | C8H5Cl2N3O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 246.05 |
| CAS Registry Number | 2089769-97-9 |
| EC Number | 826-996-4 |
| SMILES | CC1=C(NC2=C1C(=NC(=N2)Cl)Cl)C(=O)O |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Index of refraction | 1.729 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P264-P264+P265-P271-P280-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P319-P321-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P403+P233-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
|
2,4-Dichloro-5-methyl-7H-pyrrolo(2,3-d)pyrimidine-6-carboxylic acid is a heterocyclic compound that belongs to the class of pyrrolopyrimidines, a family of fused bicyclic systems that are frequently explored in medicinal chemistry for their diverse biological activities. This molecule features a pyrrolo\[2,3-d]pyrimidine core substituted with chlorine atoms at the 2- and 4-positions, a methyl group at the 5-position, and a carboxylic acid group at the 6-position, contributing to its functional versatility and chemical reactivity. The presence of halogen atoms and a carboxylic acid in a conjugated aromatic system makes it a useful scaffold in the design of small molecules with potential pharmacological applications. The compound has been investigated as a synthetic intermediate and as a potential pharmacophore in the development of inhibitors targeting kinases and other ATP-binding proteins. Pyrrolopyrimidines, especially those substituted with halogens and electron-withdrawing groups, are known to exhibit high affinity for ATP-binding pockets due to their planar aromatic structure and hydrogen bond-accepting capabilities. The dichloro substitution in this compound enhances its electron deficiency, which can improve binding interactions with amino acid residues in the active sites of enzymes. In drug discovery programs, analogs of 2,4-dichloro-5-methyl-7H-pyrrolo(2,3-d)pyrimidine-6-carboxylic acid have been studied for their inhibitory effects on various protein kinases, such as tyrosine kinases and serine/threonine kinases, many of which are dysregulated in cancer and inflammatory diseases. The core structure provides an excellent starting point for structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies aimed at improving potency, selectivity, and metabolic stability of lead compounds. The carboxylic acid group at the 6-position plays an important role in modulating the molecule's physicochemical properties. It can increase aqueous solubility, provide a site for further chemical derivatization (e.g., esterification or amide formation), and participate in ionic interactions within biological targets. In medicinal chemistry, carboxylic acids are often used to enhance target engagement and optimize pharmacokinetic properties through prodrug strategies. This compound is also used as a building block in the synthesis of larger heterocyclic molecules for pharmaceutical screening libraries. Its structural framework is conducive to modification at multiple positions, allowing medicinal chemists to generate analogs with varied steric and electronic properties. These analogs can then be tested for bioactivity in high-throughput screening assays. The synthetic accessibility of 2,4-dichloro-5-methyl-7H-pyrrolo(2,3-d)pyrimidine-6-carboxylic acid further supports its utility in research. It can be synthesized through condensation reactions involving appropriate pyrrole and chlorinated pyrimidine precursors, followed by functionalization steps to introduce the methyl and carboxylic acid substituents. These methodologies enable the generation of diverse derivatives for structure optimization. Although the compound itself has not been widely reported as a clinically approved drug, its structural motif is commonly found in several pharmaceutical agents and investigational compounds. Its incorporation into drug-like molecules has been associated with anti-cancer, anti-viral, and anti-inflammatory activities depending on the nature of the additional substituents and the biological targets involved. As research continues to focus on kinase inhibition and nucleic acid-interacting proteins, molecules such as 2,4-dichloro-5-methyl-7H-pyrrolo(2,3-d)pyrimidine-6-carboxylic acid remain valuable for developing selective inhibitors with therapeutic potential. It exemplifies the strategic design of small aromatic heterocycles that balance reactivity, biological compatibility, and synthetic flexibility. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 2,4-dichloro-5-methyl-7H-pyrrolo(2,3-d)pyrimidine-6-carboxylic acid |