Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| J&H Chemical HK Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8739-6430 8739-6432 | |||
 |
sales@jhechem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2023 | ||||
| Classification | Organic raw materials >> Carboxylic compounds and derivatives |
|---|---|
| Name | (R)-2-Amino-2-(3-bromophenyl)acetic acid |
| Synonyms | (2R)-2-amino-2-(3-bromophenyl)acetic acid |
| Molecular Structure | 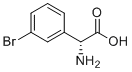 |
| Protein Sequence | X |
| Molecular Formula | C8H8BrNO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 230.06 |
| CAS Registry Number | 2166163-71-7 |
| SMILES | C1=CC(=CC(=C1)Br)[C@H](C(=O)O)N |
| Boiling point | 351.6±32.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)* |
|---|---|
| Flash point | 166.4±25.1 ºC (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details |
|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302,H315,H319,H335 Details |
| Precautionary Statements | P261,P264,P270,P271,P280,P302,P304,P321,P330,P340,P352,P362,P364,P405 Details |
| SDS | Available |
|
(R)-2-Amino-2-(3-bromophenyl)acetic acid is a chiral, non-standard amino acid derivative in which the α-carbon of glycine is substituted by a 3-bromophenyl group and bears both amino and carboxyl functionalities. The molecular formula is C8H8BrNO2, with a molecular weight of ~230.06 g mol−1 (CAS number 79422-73-4) as listed in chemical reagent databases. While the first specific disclosure of the (R)-enantiomer is not easy to trace in classical publications, the compound emerges from the broader development of arylglycines and α-aryl-α-amino acids. α-Aryl amino acids have been of interest in peptide research for at least several decades, as modifications on the α-carbon with aryl substituents enable changes in conformation, steric bulk, and side-chain properties. For example, the “α-arylglycine” motif is well known in medicinal chemistry and peptidomimetic design. More recently, articles on quaternary α-aryl-α-amino acids (Q4As) have demonstrated interest in such substituted amino acids for peptide stabilisation and novel backbone design. Although the specific 3-bromophenyl variant may not be deeply discussed in stand-alone peer-review articles, reagent chemical listings and synthetic route disclosures confirm that the compound is commercially available and used as a building block. One web-listed synthesis route describes the hydrolysis of the corresponding hydantoin derivative: 5-(3-bromophenyl)-2,4-imidazolidinedione treated with NaOH and then acidification yields 2-amino-2-(3-bromophenyl)acetic acid. The method shows the chemical accessibility of the arylglycine scaffold via hydantoin intermediates and provides evidence of the compound’s synthetic manufacture. This amino acid derivative is primarily used as a synthetic intermediate rather than as a bio-natural amino acid. Because of the 3-bromophenyl substituent, it serves in medicinal chemistry, peptide research and fine chemical synthesis where the aryl-bromine functionality can undergo further transformations (e.g., cross-coupling, metal-catalysed coupling, or diversifications) and the amino acid framework can be incorporated into peptides or ligands. The presence of the bromine atom on the phenyl ring provides a handle for further derivatisation (for example via palladium-catalysed coupling or halogen-exchange) to diversify side-chain functionality. The amino acid motif allows incorporation into peptide chains or small molecule architectures where α-aryl substitution modulates backbone conformation, hydrophobicity and electronic character. One noted use is as a reagent in the synthesis of 2-aminoimidazole-4-ones, which are of interest in medicinal chemistry (for example as modulators of cognitive impairment, Alzheimer’s disease or neurodegeneration) as referenced in supplier data. This suggests that (R)-2-Amino-2-(3-bromophenyl)acetic acid can serve as a precursor to heterocyclic motifs or more complex scaffolds by virtue of its amino acid core and aryl halide substitution. Chemically, the compound combines the reactivity typical of amino acids (amino group, carboxyl group) with the functional handle of an aryl bromide. Its carboxyl group can be activated (for example to acid chlorides, esters, amides) to build peptides or derivatives. The amino group (free or protected) allows coupling or derivatisation. The 3-bromophenyl ring adds steric bulk and a reactive site for further functionalisation. Handling of the compound must take account of typical amino acid reagent precautions: ensure dryness, avoid exposure to strong oxidisers or bases that might affect the aryl bromide, and store in a cool, dry environment. Its supply forms (e.g., salt or free acid) may require adjustment of pH or protection of the amino group during synthetic use. In terms of physical data, vendor listings indicate pure solid form, molecular formula and weight as above, with an SMILES representation O=C(O)C(N)C1=CC(Br)=CC=C1. The presence of the bromine means heavier molecular weight, altered polarity relative to simple amino acids, and likely lower solubility in water compared to unsubstituted analogues—careful solvent selection is required during handling. (R)-2-Amino-2-(3-bromophenyl)acetic acid is a valuable chiral amino acid derivative used in medicinal chemistry and peptide design. It is part of the wider class of α-aryl amino acids, which are incorporated when modification of backbone geometry or side-chain reactivity is needed. With the aryl bromide substituent, it offers a synthetic handle for further structural diversification. Though not a mainstream bio-amino acid, it serves as a powerful reagent in custom synthesis workflows. Researchers using this compound should verify stereochemical purity (R-configuration), protect the amino group if needed, and exploit the aryl halide for coupling or further functionalisation. References Jafari A, Saeidian H (2023) Green Synthesis and Bioactivity of Aliphatic N-Substituted Glycine Derivatives. ACS Omega 8(24) 21745–21756. DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c02828 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for (R)-2-Amino-2-(3-bromophenyl)acetic acid |