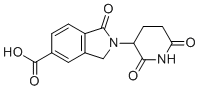
2-(2,6-Dioxopiperidin-3-yl)-1-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-isoindole-5-carboxylic acid is a complex heterocyclic compound with a fused bicyclic structure that combines an isoindole ring system with a piperidine derivative. This molecule contains a 2,6-dioxopiperidine fragment attached at the 3-position to an isoindole ring. The structure features both a carboxylic acid group at the 5-position of the isoindole ring and a carbonyl group at the 1-position of the bicyclic system.
The compound is of interest in the context of synthetic chemistry due to its unique structure, which incorporates both heteroatoms (nitrogen and oxygen) and various functional groups. The presence of a piperidine ring, a common motif in organic chemistry, suggests potential applications in medicinal chemistry and drug design. The dioxopiperidine fragment can participate in various chemical transformations, while the isoindole ring system can contribute to biological activity, as isoindoles are known to possess a range of pharmacological properties.
Synthetically, this compound can be prepared through a multi-step reaction sequence that involves the construction of the bicyclic isoindole system, followed by the functionalization of the piperidine ring with the appropriate keto and carboxylic acid groups. The dioxopiperidine group at the 3-position may be introduced via nucleophilic substitution or electrophilic aromatic substitution, depending on the reactivity of the starting materials.
In terms of biological applications, compounds incorporating both isoindole and piperidine motifs have been studied for their potential in treating neurological disorders, as well as for their activity against various enzymes and receptors. The combination of functional groups, such as the carboxyl group and the carbonyl group, may influence the pharmacodynamics of the molecule by enabling interactions with target biomolecules, including enzymes involved in metabolic processes or receptors involved in signaling pathways.
The presence of both a carboxylic acid and a carbonyl group in the structure may contribute to increased solubility in polar solvents and facilitate interactions with biological targets. Additionally, the structural complexity of the molecule might allow it to serve as a scaffold for the design of more potent derivatives through modifications of the isoindole and piperidine rings, potentially leading to compounds with improved selectivity and potency for specific therapeutic applications.
Overall, 2-(2,6-dioxopiperidin-3-yl)-1-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-isoindole-5-carboxylic acid represents a versatile scaffold in drug discovery, with potential applications in the design of bioactive molecules aimed at treating a range of diseases or modulating specific biological pathways. The functional groups present in its structure allow for a variety of synthetic modifications, enabling the development of a diverse array of compounds with possible therapeutic benefits.
|



 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details