Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Shanghai Zhuyao Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (021) 5859-6383 | |||
 |
marketing@pharmalego.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2023 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2024 | ||||
| Classification | Organic raw materials >> Heterocyclic compound >> Piperidines |
|---|---|
| Name | 3-(5-Fluoro-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione |
| Synonyms | 3-(6-fluoro-3-oxo-1H-isoindol-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione |
| Molecular Structure | 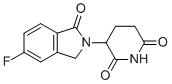 |
| Molecular Formula | C13H11FN2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 262.24 |
| CAS Registry Number | 2468780-76-7 |
| SMILES | C1CC(=O)NC(=O)C1N2CC3=C(C2=O)C=CC(=C3)F |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3, Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Index of Refraction | 1.610, Calc.* |
| Boiling Point | 547.2±50.0 ºC (760 mmHg), Calc.* |
| Flash Point | 284.7±30.1 ºC, Calc.* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details |
|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319 Details |
| Precautionary Statements | P501-P270-P264-P280-P302+P352-P337+P313-P305+P351+P338-P362+P364-P332+P313-P301+P312+P330 Details |
| SDS | Available |
|
3-(5-Fluoro-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione is a chemical compound that belongs to the class of isoindoline derivatives, which are known for their diverse biological activities. The structure of this compound features an isoindoline ring system with a fluorine atom at the 5-position, a carbonyl group at the 1-position, and a piperidine-2,6-dione moiety, which is a key functional group in its biological activity. The presence of the fluorine atom, along with the lactam ring, contributes to its stability and potential as a biologically active molecule. The discovery of 3-(5-Fluoro-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione is part of ongoing research into isoindoline derivatives for their potential therapeutic properties. Isoindolines are a class of compounds that have garnered attention in medicinal chemistry due to their ability to exhibit a wide range of biological activities, including anticancer, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory effects. By introducing halogen atoms such as fluorine, the compounds' stability, lipophilicity, and ability to bind to specific biological targets can be enhanced. In this compound, the fluorine atom serves to modify the electronic properties of the molecule, increasing its potential for interaction with various proteins and enzymes. The fluorine substitution at the 5-position of the isoindoline ring system is known to enhance the compound's metabolic stability, which is a desirable characteristic for drug candidates. Additionally, the lactam ring (piperidine-2,6-dione) has been shown to contribute to the bioactivity of isoindoline derivatives by promoting specific interactions with target receptors or enzymes involved in disease progression. This combination of functional groups makes 3-(5-Fluoro-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione a promising candidate for drug development. The compound has potential applications in the development of anticancer agents. The isoindoline scaffold is particularly attractive for cancer therapy, as it can be used to design molecules that target key enzymes or receptors involved in tumor growth and metastasis. Isoindoline derivatives like 3-(5-Fluoro-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione may serve as inhibitors of specific kinases or proteases, interfering with signaling pathways that promote cancer cell proliferation and survival. The introduction of the fluorine atom may enhance the binding affinity and selectivity of the compound, improving its efficacy in targeting cancer cells. In addition to its potential in cancer therapy, 3-(5-Fluoro-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione could also be explored for antimicrobial applications. The unique structure of the compound, with its fluorine substitution and lactam functionality, positions it as a potential inhibitor of microbial enzymes, making it valuable for the development of novel antimicrobial agents. By interfering with the function of key enzymes or proteins in pathogens, this compound may be able to disrupt their growth and survival, providing a basis for the development of new treatments for bacterial or fungal infections. Furthermore, the compound may find applications in organic synthesis, particularly as an intermediate in the preparation of other biologically active molecules. The functional groups in 3-(5-Fluoro-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione provide versatility in creating derivatives with tailored properties, making it a useful building block in the synthesis of complex chemical structures. Overall, 3-(5-Fluoro-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione is a promising compound with potential applications in drug discovery, particularly for cancer therapy and antimicrobial treatments. Its unique combination of functional groups enhances its stability and bioactivity, making it an attractive candidate for further research and development in the fields of medicinal chemistry and organic synthesis. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 3-(5-Fluoro-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione |