Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Hangzhou Verychem Science And Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8816-2785 +86 13606544505 | |||
 |
lucy@verychem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2004 | ||||
| chemBlink massive supplier since 2021 | ||||
| Classification | Flavors and spices >> Synthetic spice >> Phenols, ethers and epoxides >> Phenolic flavors |
|---|---|
| Name | Poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide) |
| Synonyms | 2,6-Dimethyl-1,4-phenylene ether homopolymer |
| Molecular Structure | 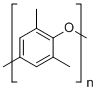 |
| Molecular Formula | [C6H2(CH3)2O]n |
| Molecular Weight | 122.16 |
| CAS Registry Number | 25134-01-4 |
| EC Number | 607-561-6 |
| SMILES | CC1=C(C(=CC=C1)C)O |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3, Calc.*, 1.15 g/mL (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Melting point | 46 ºC (Expl.) |
| Index of Refraction | 1.521, Calc.* |
| Boiling Point | 280.4±23.0 ºC (760 mmHg), Calc.*, 203 ºC (Expl.) |
| Flash Point | 112.6±20.0 ºC, Calc.*, 73 ºC (Expl.) |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |


 GHS05;GHS06;GHS09 Danger Details
GHS05;GHS06;GHS09 Danger Details | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319 Details | ||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P264-P280-P302+P352-P337+P313-P305+P351+P338-P362+P364-P332+P313 Details | ||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Transport Information | UN 2261 | ||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||
|
Poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide), commonly abbreviated as PPO, is a high-performance thermoplastic polymer known for its remarkable thermal stability, mechanical strength, and low moisture absorption. The polymer’s structure consists of repeating units of 2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide, which contribute to its rigidity and resistance to heat and chemical exposure. Originally synthesized by General Electric in the 1950s, PPO was developed as part of an effort to create materials that could maintain structural integrity at high temperatures and in challenging environments. The polymerization process for PPO typically involves oxidative coupling, in which 2,6-dimethylphenol units are linked through an oxygen bridge, resulting in a stable polymer backbone with outstanding properties. One of the primary applications of poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide) is in the electronics industry, where its thermal stability and low dielectric constant make it ideal for manufacturing electronic components and insulation materials. PPO can withstand high temperatures without degrading, which is critical for components that are subjected to constant heat and electrical currents. Additionally, it exhibits low moisture absorption, reducing the risk of material degradation over time, which enhances the lifespan of electronic devices. Another significant application of PPO is in the production of automotive parts. Due to its high impact strength, resistance to chemicals, and light weight, PPO is used to manufacture components such as engine covers, fuel system parts, and air intake manifolds. When blended with polystyrene (PS), PPO forms Noryl®, a widely used engineering plastic that provides increased flexibility and improved processability while retaining many of PPO’s original properties. This blend is particularly popular in automotive and household appliance applications, where manufacturers require materials that are both durable and easy to mold into complex shapes. In addition to electronics and automotive applications, poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide) has found use in water filtration and membrane technology. Its hydrophobic nature and resistance to chemical degradation make it suitable for creating filtration membranes, particularly for use in environments with harsh chemicals or high-temperature water. These properties have made PPO-based membranes a preferred choice for desalination processes and industrial water treatment. Overall, poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide) is an essential polymer with extensive applications across industries. Its stability, strength, and compatibility with other polymers such as polystyrene contribute to its widespread use in electronics, automotive, and water treatment sectors. Ongoing research into PPO aims to expand its applications further, particularly in emerging fields such as sustainable material design and high-performance filtration systems. References Igor V. Tetko, Vsevolod Yu. Tanchuk, Tamara N. Kasheva, and Alessandro E. P. Villa. Estimation of Aqueous Solubility of Chemical Compounds Using E-State Indices, J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci., 2001, 41 (6), pp 1488-1493 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide) |