Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Sichuan Taienkang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 15102825326 | |||
 |
sales@taienkangpharma.com | |||
 |
Skype Chat | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2020 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2024 | ||||
| Classification | Organic raw materials >> Nitrile compound |
|---|---|
| Name | (R)-3-((3-Amino-4-fluorophenyl)((cyclopropylmethyl)amino)methyl)benzonitrile oxalate |
| Molecular Structure | 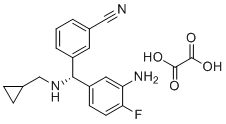 |
| Molecular Formula | C20H20FN3O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 385.39 |
| CAS Registry Number | 2602377-11-5 |
| SMILES | C(=O)(O)C(=O)O.[C@H](C1C=CC(F)=C(N)C=1)(C1C=CC=C(C#N)C=1)NCC1CC1 |
|
(R)-3-((3-Amino-4-fluorophenyl)((cyclopropylmethyl)amino)methyl)benzonitrile oxalate is a chemical compound that features a complex structure incorporating a benzonitrile core, a fluorophenyl group, an amino group, and a cyclopropylmethylamino side chain. The inclusion of a fluorine atom and a cyclopropyl group makes this compound of particular interest in medicinal chemistry, as it may exhibit unique interactions with biological targets, leading to potential therapeutic applications. The oxalate salt form enhances its solubility and stability, important attributes for its potential use in pharmaceutical development. The discovery of (R)-3-((3-Amino-4-fluorophenyl)((cyclopropylmethyl)amino)methyl)benzonitrile oxalate is part of ongoing research into molecules that can selectively target receptors or enzymes involved in various diseases, particularly in the context of neurological or metabolic disorders. The fluorophenyl group provides a means to enhance lipophilicity, aiding in the compound's ability to cross cell membranes and interact with hydrophobic regions of enzymes or receptors. Additionally, the cyclopropylmethylamino group, known for its ability to confer stability and improve receptor binding, may contribute to the compound's overall biological activity. The synthesis of (R)-3-((3-Amino-4-fluorophenyl)((cyclopropylmethyl)amino)methyl)benzonitrile oxalate typically involves multiple steps. The process begins with the formation of the benzonitrile scaffold, followed by the introduction of the 3-amino-4-fluorophenyl and cyclopropylmethylamino groups. The stereochemistry is carefully controlled to obtain the (R)-enantiomer, which is important for optimizing the compound's biological activity. The final step in the synthesis involves the formation of the oxalate salt to improve the compound’s solubility, making it suitable for further biological testing. In terms of application, (R)-3-((3-Amino-4-fluorophenyl)((cyclopropylmethyl)amino)methyl)benzonitrile oxalate holds promise in drug discovery, particularly in areas involving central nervous system disorders or other diseases where modulation of specific receptor systems is crucial. The presence of both the amino and fluorophenyl groups suggests potential activity in modulating neurotransmitter systems, such as serotonin or dopamine receptors, which are implicated in conditions like depression, anxiety, or Parkinson's disease. Additionally, the cyclopropylmethyl group may enhance the compound's ability to interact with proteins involved in inflammation or cancer, adding further versatility to its therapeutic potential. Further studies are needed to explore the compound's pharmacokinetic properties, including absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, as well as its efficacy in preclinical disease models. Understanding the interaction of (R)-3-((3-Amino-4-fluorophenyl)((cyclopropylmethyl)amino)methyl)benzonitrile oxalate with various biological targets will provide insight into its potential as a therapeutic agent. Research into its selectivity and potency will guide the development of derivatives with improved pharmacological profiles. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for (R)-3-((3-Amino-4-fluorophenyl)((cyclopropylmethyl)amino)methyl)benzonitrile oxalate |