Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Luminescence Technology Corp. | Taiwan | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+886 (2) 2697-5600 | |||
 |
sales@lumtec.com.tw | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1999 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2024 | ||||
| Classification | Organic raw materials >> Organic phosphine compound |
|---|---|
| Name | (4-(3,6-Dimethoxy-9h-carbazol-9-yl)butyl)phosphonic acid |
| Synonyms | MeO-4PACz |
| Molecular Structure | 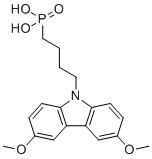 |
| Molecular Formula | C18H22NO5P |
| Molecular Weight | 363.34 |
| CAS Registry Number | 2922526-56-3 |
| EC Number | 978-553-0 |
| SMILES | COC1=CC2=C(C=C1)N(C3=C2C=C(C=C3)OC)CCCCP(=O)(O)O |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319 Details | ||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P264-P264+P265-P280-P302+P352-P305+P351+P338-P321-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364 Details | ||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||
|
The compound (4-(3,6-dimethoxy-9H-carbazol-9-yl)butyl)phosphonic acid is a specially designed molecule that combines the carbazole core’s robust photophysical properties with a phosphonic acid group, enabling applications in advanced materials science. The dimethoxy substitution enhances the compound’s electron-donating capabilities, thermal stability, and solubility, making it an attractive candidate for use in optoelectronics and surface modification technologies. The carbazole moiety, a nitrogen-containing aromatic structure, has been widely explored in the development of organic semiconductors and light-emitting materials. The dimethoxy groups at the 3- and 6-positions of the carbazole enhance its electronic properties by extending the conjugation and fine-tuning the electronic bandgap. This modification has proven crucial for optimizing the efficiency of light-harvesting and charge-transporting systems. The attachment of a butyl linker terminating in a phosphonic acid group provides the compound with strong adhesion capabilities to metal oxide surfaces, a critical feature for applications in layered electronic devices. This compound’s discovery is tied to research into materials for organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs). In OLED devices, (4-(3,6-dimethoxy-9H-carbazol-9-yl)butyl)phosphonic acid functions effectively as a hole-transporting material. Its carbazole backbone facilitates charge mobility, reducing energy losses during recombination, while the phosphonic acid group ensures stable attachment to indium tin oxide (ITO) and other electrode surfaces. This results in improved device efficiency and durability, key challenges in developing high-performance OLED displays and lighting systems. Another critical application area is in dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs). The compound can act as a surface modifier for titanium dioxide photoanodes, enhancing dye anchoring and electron transfer efficiency. By improving the interface quality between the dye and the electrode, it contributes to higher energy conversion efficiencies in DSSCs. Research continues to optimize its application in this context, addressing the need for cost-effective and sustainable photovoltaic solutions. (4-(3,6-Dimethoxy-9H-carbazol-9-yl)butyl)phosphonic acid is also being explored for its role in photocatalytic systems. The carbazole’s capacity for light absorption and electron transfer, combined with the phosphonic acid group’s strong binding to catalytic surfaces, makes it a promising candidate for use in photocatalytic water splitting and pollutant degradation. Beyond its current applications, ongoing studies are investigating its potential in bioelectronics and sensing technologies. The combination of its robust photophysical properties, stability, and functional versatility positions it as a valuable material for emerging technologies in energy and environmental science. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for (4-(3,6-Dimethoxy-9h-carbazol-9-yl)butyl)phosphonic acid |