Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Shandong Juntai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 15106953682 | |||
 |
sales01@h2opharm.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2020 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2024 | ||||
| Classification | Biochemical >> Common amino acids and protein drugs |
|---|---|
| Name | Pal-Glu(OSu)-OH |
| Synonyms | (2S)-5-(2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)oxy-2-(hexadecanoylamino)-5-oxopentanoic acid |
| Molecular Structure | 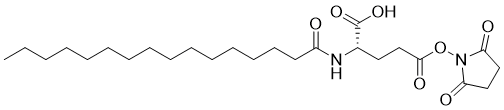 |
| Protein Sequence | X |
| Molecular Formula | C25H42N2O7 |
| Molecular Weight | 482.61 |
| CAS Registry Number | 294855-91-7 |
| SMILES | CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)N[C@@H](CCC(=O)ON1C(=O)CCC1=O)C(=O)O |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3, Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Index of Refraction | 1.515, Calc.* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details |
|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319 Details |
| Precautionary Statements | P501-P270-P264-P280-P302+P352-P337+P313-P305+P351+P338-P362+P364-P332+P313-P301+P312+P330 Details |
| SDS | Available |
|
Pal-Glu(OSu)-OH is a synthetic chemical compound used primarily in peptide modification, especially in lipidation processes for therapeutic applications. The structure of Pal-Glu(OSu)-OH consists of a palmitoyl (Pal) group, which is a long-chain fatty acid, attached to the amino acid glutamic acid (Glu). The (OSu) group stands for N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) ester, a widely used functional group in biochemical applications due to its ability to efficiently react with primary amine groups. The (OH) at the end of the structure represents a hydroxyl group, which may influence its solubility and reactivity. Pal-Glu(OSu)-OH is part of a family of compounds that enable the lipidation of peptides, a modification that enhances the hydrophobicity of peptides and increases their affinity for lipid membranes. This lipidation has critical implications for drug delivery, membrane interaction, and protein stability. The NHS ester in Pal-Glu(OSu)-OH allows for selective attachment of the palmitoyl chain to peptides or proteins containing free amine groups, making it useful in both laboratory research and pharmaceutical applications. The discovery of compounds like Pal-Glu(OSu)-OH emerged from the need to enhance peptide-based therapies. Peptides, while potent and selective, often suffer from rapid degradation and poor bioavailability when administered in biological systems. By lipidating peptides, researchers discovered that they could significantly improve their stability, half-life, and ability to penetrate biological membranes. Palmitoylation, in particular, helps peptides interact with cell membranes more effectively, improving their pharmacological properties. Pal-Glu(OSu)-OH is widely used in drug development, particularly for improving the pharmacokinetics of therapeutic peptides. Palmitoylation of peptides using Pal-Glu(OSu)-OH can increase their half-life in the bloodstream, reduce enzymatic degradation, and enhance their ability to cross biological membranes. This has proven particularly valuable for peptides used in cancer therapy, metabolic disorders, and antimicrobial treatments. In addition to its role in drug delivery, Pal-Glu(OSu)-OH is also employed in vaccine development. Lipidated peptides synthesized using this compound can elicit a stronger immune response, making them useful as components of subunit vaccines. By anchoring peptides to lipid membranes, these vaccine candidates can better mimic the natural presentation of antigens, promoting a more effective immune response. Pal-Glu(OSu)-OH also has applications in studying protein-lipid interactions. Researchers use this compound to modify peptides or proteins to study their behavior in lipid environments, particularly for membrane proteins. By attaching a lipid chain to the peptide, it can integrate into or interact with lipid bilayers, allowing for more accurate modeling of membrane-associated biological processes. Overall, Pal-Glu(OSu)-OH is a versatile tool in chemical biology, particularly in peptide modification for therapeutic and research applications. Its role in enhancing peptide stability, facilitating membrane interactions, and promoting immune responses underscores its importance in modern drug development and molecular research. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Pal-Glu(OSu)-OH |