Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Shanghai Worldyang Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13651600618 +86 (21) 5679-5779 | |||
 |
sales7777@worldyachem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: 13651600618 | |||
 |
WhatsApp: +86 13651600618 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink premium supplier since 2023 | ||||
| Classification | Chemical reagent >> Organic reagent >> Thiol/thiophenol |
|---|---|
| Name | Methyl phenyl sulfone |
| Synonyms | (Methylsulphonyl)benzene |
| Molecular Structure | 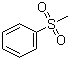 |
| Molecular Formula | C7H8O2S |
| Molecular Weight | 156.20 |
| CAS Registry Number | 3112-85-4 |
| EC Number | 221-476-8 |
| SMILES | CS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 |
| Melting point | 85-88 ºC |
|---|---|
| Water solubility | insoluble |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P264-P270-P301+P317-P330-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Methyl phenyl sulfone, also known as methyl phenyl sulfone (MPS) or simply sulfone, is an organic compound recognized for its robustness and wide range of applications in chemical synthesis and industry. Methyl phenyl sulfone was first discovered during the study of sulfone chemistry in the early 20th century. Its synthesis involves the oxidation of methyl phenyl sulfide. The process can be carried out efficiently under controlled conditions using oxidizing agents such as hydrogen peroxide or peracids to produce high purity sulfones. The chemical structure of methyl phenyl sulfone consists of a sulfonyl group (-SO2-) and a methyl group (-CH3) flanking the benzene ring (-C6H5). This combination imparts stability and unique chemical properties to the compound, making it useful in a variety of applications. Methyl phenyl sulfone is a crystalline solid at room temperature with a melting point of approximately 82-85ºC. It is soluble in organic solvents such as acetone, benzene, and diethyl ether, but slightly soluble in water. The presence of the sulfonyl group contributes to its thermal and chemical stability, allowing it to withstand harsh conditions that may degrade other organic molecules. Methyl phenyl sulfone is a key intermediate in organic synthesis. It is used to prepare a variety of heterocyclic compounds and in processes such as the Julia-Kocienski olefination, a method for forming carbon-carbon double bonds (olefins). In this reaction, MPS acts as a precursor to phenylsulfonyl anions, which can be alkylated and subsequently converted to olefins, facilitating the synthesis of complex organic molecules. In pharmaceutical chemistry, MPS is used to synthesize active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Its stability and functional group versatility make it suitable for creating a variety of drug scaffolds, especially those that require a strong chemical backbone. The thermal stability of methyl phenyl sulfone also makes it valuable in the production of high-performance polymers and materials. It is used to synthesize polysulfones and polyethersulfones, which are known for their strength, oxidation resistance, and ability to maintain integrity at high temperatures. These properties make such polymers ideal for applications in aerospace, electronics, and membrane technology. MPS is also used in environmental chemistry, especially in applications that require durable and non-reactive substances. Its ability to act as a solvent or reagent in certain industrial processes highlights its versatility and usefulness in various chemical industries. References 2021. High Chemoselectivity in the Construction of Aryl Methyl Sulfones via an Unexpected C-S Bond Formation between Sulfonylhydrazides and Dimethyl Phosphite. Synthesis, 53(24). DOI: 10.1055/a-1581-2271 2022. Recyclable Hypervalent Iodine Reagents in Modern Organic Synthesis. Synthesis, 54(22). DOI: 10.1055/s-0041-1737909 2022. Photoredox-Mediated Desulfonylative Radical Reactions: An Excellent Approach Towards C-C and C-Heteroatom Bond Formation. Synthesis, 54(24). DOI: 10.1055/a-1900-8895 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Methyl phenyl sulfone |