Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Shanghai ZaiQi Bio-Tech Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (21) 5482-4098 | |||
 |
sales1@chemzq.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2004 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2009 | ||||
| Classification | Organic raw materials >> Ketone compound |
|---|---|
| Name | 7-Hydroxy-6-methyl-3H-phenoxazin-3-one |
| Molecular Structure | 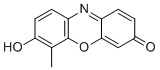 |
| Molecular Formula | C13H9NO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 227.22 |
| CAS Registry Number | 326493-57-6 |
| SMILES | CC1=C(C=CC2=C1OC3=CC(=O)C=CC3=N2)O |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 405.2±45.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)* |
| Flash point | 198.9±28.7 ºC (Calc.)* |
| Index of refraction | 1.678 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
|
Lipase detection is an essential process in both clinical diagnostics and microbial product evaluation. Lipases are enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of fats and play key roles in digestion and metabolic regulation. Accurate measurement of lipase activity is critical in assessing pancreatic function, monitoring disease progression, and optimizing microbial production of lipase-related compounds such as lipstatin. High-throughput screening (HTS) assays have been developed to accelerate the evaluation of lipase production by microbial strains. A recent study demonstrated the development and optimization of an HTS assay for the rapid assessment of lipstatin production in various *Streptomyces* strains. The assay was designed to provide reproducible, quantitative measurements in a short timeframe, allowing multiple strains to be tested simultaneously. This methodology relied on the detection of enzymatic activity using chromogenic or fluorogenic substrates, which generate measurable signals proportional to lipase concentration. The optimization included adjusting assay conditions such as pH, temperature, and substrate concentration to maximize sensitivity and accuracy. The use of HTS facilitates the identification of high-producing strains and accelerates the selection process in industrial microbial fermentation. In clinical diagnostics, the measurement of pancreatic lipase and related enzymes is important for evaluating pancreatic function in patients. Studies have quantified pancreatic elastase-1 concentrations in duodenal aspirates from healthy individuals and patients with chronic pancreatitis. Enzymatic activity assays provide insights into enzyme secretion and function, which is crucial for diagnosing exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. Reliable detection of pancreatic enzymes allows for timely intervention and improved patient management. The methodologies employed typically involve collection of duodenal aspirates, followed by enzyme-specific detection techniques that provide precise quantitative data. These methods enable differentiation between normal and pathological conditions, supporting clinical decision-making. Technological advancements in lipase detection have also led to the development of specialized devices and kits. Devices and methods for detecting pancreatic lipase are designed for both research and clinical applications. Such systems include kits for quantitative detection of lipase, enabling rapid, accurate, and reproducible measurement of enzyme levels in biological samples. Some kits are based on colorimetric or fluorescent readouts, which simplify the interpretation of results. A serum lipase detection kit, for example, includes reagents and protocols optimized for clinical testing, providing standardized and reproducible results. These kits have been granted patents, ensuring validated and commercially available tools for laboratory and clinical use. Fluorescent indicators with large Stokes shifts represent another advancement in enzymatic detection. Fluorescent metal ion indicators can be used to design highly sensitive assays for lipase activity. Large Stokes shift fluorescent molecules minimize background interference and improve the accuracy of detection. These indicators can be integrated into automated platforms, facilitating high-throughput analyses and reducing the need for extensive sample preparation. Such tools are particularly valuable in both industrial microbiology and biomedical research, where precise enzymatic measurements are required. The combination of high-throughput assays, clinical detection kits, and fluorescent indicators provides a robust toolkit for studying lipase activity in multiple contexts. In microbial biotechnology, these tools support strain selection, fermentation optimization, and metabolite analysis. In clinical settings, they aid in the diagnosis and monitoring of pancreatic disorders. Together, these technologies enhance both research efficiency and patient care. References Rodrigues ME, da Costa SS, Sakamoto IK, et al. (2017) Development and Optimization of a High-Throughput Screening Assay for Rapid Evaluation of Lipstatin Production by Streptomyces Strains. Current Microbiology 75, 1585–1594. DOI: 10.1007/s00284-017-1420-x Venglovecz V, Rakonczay Z, Hegyi P, et al. (2004) Analysis of Pancreatic Elastase-1 Concentrations in Duodenal Aspirates from Healthy Subjects and Patients with Chronic Pancreatitis. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 49, 1403–1410. DOI: 10.1023/b:ddas.0000042238.80040.cc |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 7-Hydroxy-6-methyl-3H-phenoxazin-3-one |