Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Shandong Benrite New Chemical Materials Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (0533) 286-6658 | |||
 |
sales@benritechem.com | |||
 |
Skype Chat | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: benritechem | |||
 |
WhatsApp: +8613021512891 | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2024 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2024 | ||||
| Classification | Organic raw materials >> Organic phosphine compound |
|---|---|
| Name | Ethoxy(pentafluoro)cyclotriphosphazene |
| Synonyms | 2-ethoxy-2,4,4,6,6-pentafluoro-1,3,5-triaza-2?5,4?5,6?5-triphosphacyclohexa-1,3,5-triene |
| Molecular Structure | 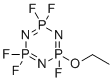 |
| Molecular Formula | C2H5F5N3OP3 |
| Molecular Weight | 274.99 |
| CAS Registry Number | 33027-66-6 |
| EC Number | 608-823-2 |
| SMILES | CCOP1(=NP(=NP(=N1)(F)F)(F)F)F |
| Solubility | 237.4 mg/L (25 ºC water) |
|---|---|
| Density | 2.1±0.1 g/cm3, Calc.* |
| Index of Refraction | 1.511, Calc.* |
| Melting point | 50.04 ºC |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |

 GHS05;GHS09 Danger Details
GHS05;GHS09 Danger Details | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H314-H411 Details | ||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P501-P273-P264-P280-P391-P303+P361+P353-P301+P330+P331-P363-P304+P340+P310-P305+P351+P338+P310-P405 Details | ||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||
|
Ethoxy(pentafluoro)cyclotriphosphazene is a specialized compound within the class of cyclotriphosphazenes, which are known for their intriguing structure and diverse applications. The molecule consists of a six-membered ring with alternating phosphorus and nitrogen atoms, where one phosphorus atom is substituted by an ethoxy group and the remaining phosphorus atoms are bonded to pentafluoro groups. This combination of substituents provides the molecule with unique physical and chemical properties, particularly thermal stability, chemical resistance, and the potential for functionalization. Cyclotriphosphazenes were first identified in the early 19th century, with research significantly advancing in the mid-20th century when synthetic methods for producing substituted cyclotriphosphazenes became more refined. The discovery of ethoxy(pentafluoro)cyclotriphosphazene can be linked to the exploration of organophosphorus chemistry, particularly in the development of materials that require high thermal and chemical resistance. Researchers have found that introducing fluoroalkyl and ethoxy groups into the cyclotriphosphazene framework provides a balance of hydrophobicity, reactivity, and structural integrity. One of the primary applications of ethoxy(pentafluoro)cyclotriphosphazene is in the field of advanced materials, especially as a component in the synthesis of flame-retardant polymers. The high phosphorus and fluorine content of this compound makes it an effective flame retardant, as phosphorus-containing materials help to reduce flammability by promoting char formation, while fluorine imparts heat resistance and limits the production of flammable gases. These flame-retardant materials are used in industries where fire safety is critical, such as electronics, aerospace, and automotive manufacturing. Another significant use of ethoxy(pentafluoro)cyclotriphosphazene is in the development of high-performance lubricants. The fluorinated substituents confer exceptional chemical inertness and low surface energy, making these lubricants suitable for applications in extreme environments, such as high temperatures, high pressures, and chemically reactive settings. Such lubricants are employed in aerospace engineering, where they help reduce wear and tear on mechanical components operating under demanding conditions. In addition, ethoxy(pentafluoro)cyclotriphosphazene serves as a precursor for functionalized phosphazene polymers. These polymers have applications in membranes, coatings, and elastomers due to their versatility, chemical resistance, and ability to incorporate a wide range of substituents. Researchers have used this compound to design membranes for gas separation and ion transport, which are important in energy storage and water purification technologies. The combination of ethoxy and pentafluoro groups allows for precise tuning of the material’s hydrophobicity and mechanical properties. Ethoxy(pentafluoro)cyclotriphosphazene is also valuable in the synthesis of specialty chemicals for pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals. The phosphorus-nitrogen backbone can be functionalized to introduce bioactive moieties, while the ethoxy and fluoro groups can modify the compound’s solubility and metabolic stability. Such derivatives are being investigated for their potential in drug delivery systems and as intermediates in the synthesis of novel therapeutic agents. Recent advancements in synthetic methods have improved the efficiency of producing ethoxy(pentafluoro)cyclotriphosphazene. Techniques involving selective substitution of cyclotriphosphazene rings allow for the controlled introduction of ethoxy and fluoro groups, enhancing the ability to tailor the molecule for specific applications. This progress has broadened the potential uses of this compound in both academic research and industrial applications. Research into the applications of ethoxy(pentafluoro)cyclotriphosphazene continues to evolve, driven by the need for high-performance materials and innovative chemical solutions. Its unique structure and properties make it a key compound in the development of advanced technologies across multiple fields. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Ethoxy(pentafluoro)cyclotriphosphazene |