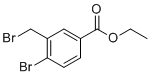
The chemical substance benzoic acid, 4-bromo-3-(bromomethyl)-, ethyl ester, also known as ethyl 4-bromo-3-(bromomethyl)benzoate, is a dihalogenated benzoic acid derivative with an ethyl ester group, recognized in organic chemistry as a versatile synthetic intermediate, particularly in pharmaceutical and materials chemistry. Its discovery and applications are well-documented in the literature, rooted in the development of substituted aromatic compounds and regioselective halogenation techniques.
The origins of this compound are tied to the study of benzoic acid derivatives, which have been explored since the 19th century for their reactivity and utility as synthetic building blocks. The introduction of bromine substituents, particularly at the 4-position and on a methyl group at the 3-position, became feasible in the early 20th century with advances in electrophilic and radical halogenation methods. The ethyl ester group, commonly used to protect carboxylic acids, was widely adopted in the mid-20th century for its ease of formation and hydrolysis. The specific combination of 4-bromo and 3-(bromomethyl) substituents on an ethyl benzoate emerged in the late 20th century, driven by the pharmaceutical industry’s need for reactive, multifunctional intermediates to construct complex molecules. Advances in regioselective bromination during the 1960s and 1970s enabled the precise synthesis of such compounds.
Synthetically, ethyl 4-bromo-3-(bromomethyl) syntax error, unexpected '(', expecting identifier (T_IDENTIFIER) or variable (T_VARIABLE) or '{' or '$'benzoate is typically prepared through a multi-step process. A common route starts with 4-bromo-3-methylbenzoic acid, which is esterified with ethanol under acidic conditions (e.g., using sulfuric acid or a Fischer esterification protocol) to form ethyl 4-bromo-3-methylbenzoate. The methyl group at the 3-position is then selectively brominated using N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) in the presence of a radical initiator, such as benzoyl peroxide or AIBN, under light or heat to yield the bromomethyl group. Alternatively, the synthesis can begin with 3-methylbenzoic acid, followed by sequential bromination at the 4-position (via electrophilic aromatic substitution) and the methyl group (via radical bromination), with esterification as the final step. These steps rely on well-established protocols in aromatic halogenation, radical chemistry, and esterification, ensuring regioselectivity and high yields.
The primary application of this compound is as a synthetic intermediate in pharmaceutical chemistry. The benzoic acid core, modified with bromine substituents, provides a rigid aromatic scaffold suitable for binding to biological targets. The 4-bromo group serves as a handle for cross-coupling reactions, such as Suzuki-Miyaura or Heck couplings, allowing the introduction of aryl, alkenyl, or alkynyl groups. The 3-(bromomethyl) group is highly reactive in nucleophilic substitution reactions, enabling the attachment of amines, thiols, or carbon nucleophiles. The ethyl ester protects the carboxylic acid, allowing selective transformations, and can be hydrolyzed to the free acid for further functionalization, such as amide formation. This compound is frequently used in the synthesis of drug candidates, including anti-inflammatory agents, kinase inhibitors, and receptor modulators, where the dihalogenated aromatic structure enhances target affinity and pharmacokinetic properties.
In materials chemistry, the compound is employed to synthesize functionalized polymers or ligands, where the bromine groups facilitate cross-coupling or substitution to build complex architectures. In academic research, it serves as a model for studying regioselective bromination, radical chemistry, and cross-coupling mechanisms. Its synthesis has contributed to the optimization of selective halogenation and esterification techniques.
The significance of ethyl 4-bromo-3-(bromomethyl)benzoate lies in its role as a multifunctional intermediate that combines the synthetic versatility of dihalogenated aromatics with the reactivity of an ethyl ester. Its development reflects progress in regioselective halogenation and aromatic chemistry. By enabling the efficient synthesis of complex, biologically active molecules, it has become a critical tool in advancing pharmaceutical, materials, and chemical research.
|



 GHS07;GHS08 Warning Details
GHS07;GHS08 Warning Details