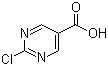
2-Chloropyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid is a chemical compound that belongs to the class of heterocyclic organic compounds. It consists of a pyrimidine ring structure, which contains two nitrogen atoms, with a carboxylic acid group (-COOH) attached at the 5-position and a chlorine atom attached at the 2-position.
The structure of 2-chloropyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid makes it a useful intermediate in the synthesis of various pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and other organic compounds. Pyrimidine derivatives, in general, are of significant interest in medicinal chemistry due to their biological activity. The presence of both a chloro group and a carboxylic acid group in this compound contributes to its reactivity and versatility in organic synthesis.
One of the key applications of 2-chloropyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid is as a building block in the synthesis of bioactive molecules. The compound is often used in the preparation of nucleoside analogs, which are important in the development of antiviral and anticancer drugs. Pyrimidine-based compounds are frequently involved in the inhibition of enzymes like thymidylate synthase, which is essential in DNA synthesis, making these derivatives potential targets for cancer therapy.
In addition to its use in medicinal chemistry, 2-chloropyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid is also employed in the synthesis of agrochemicals, including herbicides and pesticides. The pyrimidine ring structure is known to have some herbicidal activity, and the chloro and carboxylic acid functional groups enhance the reactivity and potential for selective chemical modification. As a result, this compound can be utilized in the development of crop protection agents.
2-Chloropyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid also serves as a useful intermediate in the preparation of various materials. The pyrimidine ring system, along with the carboxyl group, can be further functionalized to create new materials with electronic, optical, or catalytic properties. Pyrimidine-based compounds are explored for their potential in the creation of organic semiconductors, photovoltaic materials, and conducting polymers.
In summary, 2-chloropyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid is an important intermediate in organic synthesis, particularly in the fields of medicinal chemistry, agrochemicals, and materials science. Its structure, which includes a pyrimidine ring with a chlorine atom and a carboxyl group, makes it a versatile building block for the development of biologically active compounds, herbicides, and advanced materials.
References
2019. Protocols for NMR Analysis in Livestock Metabolomics. Methods in Molecular Biology, 1996.
DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9488-5_23
|
























 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details