Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Suzhou Myland Pharm & Nutrition Inc. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (512) 6615-0687 | |||
 |
info@mylandpharm.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2013 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2014 | ||||
| Classification | Pharmaceutical intermediate >> Heterocyclic compound intermediate >> Pyrimidine compound >> Amine |
|---|---|
| Name | Spermine dihydrate |
| Synonyms | Gerontine; Musculamine; N,N'-Bis(3-aminopropyl)-1,4-diaminobutane; Neuridine |
| Molecular Structure | 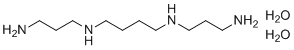 |
| Molecular Formula | C10H30N4O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 238.37 |
| CAS Registry Number | 403982-64-9 |
| EC Number | 687-801-4 |
| SMILES | C(CCNCCCN)CNCCCN.O.O |
| Melting point | 63-64 ºC (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Solubility | H2O 1 M (20 ºC) (Expl.) |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS05 Danger Details
GHS05 Danger Details | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H314 Details | ||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P260-P264-P280-P301+P330+P331-P302+P361+P354-P304+P340-P305+P354+P338-P316-P321-P363-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||
|
Spermine dihydrate is a hydrated form of spermine, a naturally occurring polyamine with the chemical formula C10H26N4·2H2O. It consists of a linear aliphatic chain containing four amino groups and two associated water molecules. Spermine is endogenously synthesized in living cells and plays a vital role in cellular metabolism, gene regulation, and structural stabilization of nucleic acids. The dihydrate form is commonly used in biochemical and molecular biology research due to its improved handling and stability in solid form. The discovery of spermine dates back to the 17th century, when it was first identified as a crystalline substance in human semen. Its chemical structure was elucidated in the 20th century, and it was found to be one of the key polyamines present in eukaryotic cells. Along with its precursor spermidine, spermine is synthesized from ornithine and methionine through the polyamine biosynthetic pathway. It is ubiquitously found in all living cells and is particularly abundant in rapidly proliferating tissues. Spermine interacts strongly with nucleic acids, particularly DNA and RNA, through electrostatic binding to the negatively charged phosphate backbone. This interaction helps stabilize the helical structure of DNA and contributes to chromatin condensation and gene expression regulation. In ribosomes, spermine is essential for maintaining the structural integrity of RNA and supporting translational efficiency. The dihydrate form of spermine is prepared by crystallization under controlled humidity conditions, allowing the incorporation of two water molecules per spermine molecule. This form is advantageous for storage and preparation of aqueous solutions in laboratory settings, as it is more stable and less hygroscopic than the anhydrous form. Spermine dihydrate is widely used in research applications involving nucleic acid structure and function. It is employed in studies of DNA compaction, chromatin organization, and the effects of polyamines on transcription and replication. In molecular biology, spermine is included in certain DNA polymerase buffers to enhance PCR efficiency by stabilizing DNA templates. In addition to its nucleic acid-related functions, spermine modulates ion channels, regulates enzyme activity, and plays a role in cell growth and apoptosis. It has been implicated in a variety of physiological processes, including embryonic development, immune response, and aging. Elevated or depleted levels of intracellular polyamines are associated with pathological conditions such as cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and metabolic disorders. In experimental therapeutics, spermine and its analogs are being investigated for potential use in anticancer strategies. Targeting the polyamine biosynthetic pathway or modulating polyamine transport has shown promise in limiting tumor cell proliferation. Additionally, spermine conjugates have been designed to enhance drug delivery and specificity for DNA-targeting agents. Spermine also serves as a model compound in the study of polycationic interactions with negatively charged biopolymers, lipids, and membranes. It is used in formulations for gene delivery vectors and in the development of nanostructured materials, where its multivalent cationic nature facilitates complex formation and cellular uptake. In summary, spermine dihydrate is a stable, hydrated form of the natural polyamine spermine, essential for nucleic acid stabilization and cell function. It is widely used in biochemical research, molecular biology, and studies of gene expression, with ongoing interest in its biomedical and pharmaceutical applications. References 2022. Structure of human spermine oxidase in complex with a highly selective allosteric inhibitor. Communications Biology, 5(1). DOI: 10.1038/s42003-022-03735-9 2022. Common synaptic phenotypes arising from diverse mutations in the human NMDA receptor subunit GluN2A. Communications Biology, 5(1). DOI: 10.1038/s42003-022-03115-3 2011. An iterative workflow for mining the human intestinal metaproteome. BMC Genomics, 12(1). DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-6 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Spermine dihydrate |