Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Shanghai Worldyang Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13651600618 +86 (21) 5679-5779 | |||
 |
sales7777@worldyachem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: 13651600618 | |||
 |
WhatsApp: +86 13651600618 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink premium supplier since 2023 | ||||
| Classification | Organic raw materials >> Organometallic compound >> Organic palladium |
|---|---|
| Name | Bis(tri-o-tolylphosphine)palladium(II) dichloride |
| Synonyms | Dichlorobis(tri-o-tolylphosphine)palladium(II) |
| Molecular Structure | 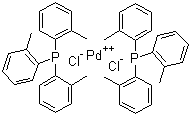 |
| Molecular Formula | C42H42Cl2P2Pd |
| Molecular Weight | 786.06 |
| CAS Registry Number | 40691-33-6 |
| EC Number | 664-487-7 |
| SMILES | CC1=CC=CC=C1P(C2=CC=CC=C2C)C3=CC=CC=C3C.CC1=CC=CC=C1P(C2=CC=CC=C2C)C3=CC=CC=C3C.Cl[Pd]Cl |
| Melting point | 280 ºC (dec.) |
|---|---|
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305+P351+P338 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Bis(tri-o-tolylphosphine)palladium(II) dichloride is a square-planar palladium complex widely used as a catalyst precursor in organometallic chemistry and homogeneous catalysis. Its molecular formula is \[PdCl2(P(o-tolyl)3)2], where the palladium(II) center is coordinated by two chloride ligands and two tri(o-tolyl)phosphine ligands. Each tri(o-tolyl)phosphine ligand contains a phosphorus atom bonded to three ortho-methylphenyl (o-tolyl) groups, which confer steric bulk and modify the electronic properties of the ligand. The compound belongs to a class of palladium(II) phosphine complexes that are frequently employed in cross-coupling reactions. The synthesis of bis(tri-o-tolylphosphine)palladium(II) dichloride is typically achieved by reacting palladium(II) chloride with two equivalents of tri(o-tolyl)phosphine in an organic solvent such as dichloromethane, tetrahydrofuran, or ethanol. The reaction yields a yellow to light orange crystalline solid that is stable under inert conditions and can be stored in dry environments for extended periods. The square-planar geometry around the palladium center is characteristic of d8 metal ions such as Pd(II). In this complex, the bulky o-tolyl substituents on the phosphine ligands play a crucial role in influencing the reactivity and selectivity of the catalyst. The steric hindrance introduced by the ortho-methyl groups can slow down ligand exchange and reductive elimination steps in catalytic cycles, which may be advantageous in controlling unwanted side reactions or enhancing regioselectivity in coupling processes. Bis(tri-o-tolylphosphine)palladium(II) dichloride has been applied extensively in palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions, particularly in the Heck, Suzuki–Miyaura, and Stille reactions. In these transformations, the complex acts as a pre-catalyst that is reduced in situ to a palladium(0) species, which then participates in oxidative addition to aryl or vinyl halides. The bulky tri(o-tolyl)phosphine ligands can stabilize reactive intermediates, prevent dimerization of palladium species, and tune the rate of key steps such as oxidative addition and reductive elimination. The complex is also useful in carbon–carbon and carbon–heteroatom bond-forming reactions, including amination, alkoxylation, and cyanation. In some cases, the use of sterically demanding phosphine ligands can improve the performance of the catalyst in reactions involving hindered or electron-rich substrates. From a practical perspective, bis(tri-o-tolylphosphine)palladium(II) dichloride is soluble in common organic solvents such as dichloromethane, chloroform, and toluene. It is sensitive to light and moisture, and therefore should be handled under an inert atmosphere, typically nitrogen or argon. The compound may decompose in the presence of strong acids or bases, or when exposed to air for extended periods. Characterization of the complex is typically performed using techniques such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, which provides information about the phosphorus environment and symmetry of the complex, and X-ray crystallography, which confirms the coordination geometry and bond lengths around the palladium center. Elemental analysis and infrared (IR) spectroscopy are also used to confirm the composition and purity of the compound. In summary, bis(tri-o-tolylphosphine)palladium(II) dichloride is a valuable palladium(II) complex with significant applications in homogeneous catalysis. Its bulky phosphine ligands modulate the reactivity of the metal center and enable high selectivity in a wide range of cross-coupling and bond-forming reactions. Its well-defined structure, combined with reliable reactivity, makes it an important tool in synthetic and organometallic chemistry. References 2024. Recent developments in the chemistry of Negishi coupling: a review. Chemical Papers, 78(3). DOI: 10.1007/s11696-024-03369-7 2021. Negishi Coupling. Science of Synthesis. URL: https://science-of-synthesis.thieme.com/app/text/?id=SD-106-00217 2013. Palladium-Catalyzed Arylation. Science of Synthesis. URL: https://science-of-synthesis.thieme.com/app/text/?id=SD-126-00064 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Bis(tri-o-tolylphosphine)palladium(II) dichloride |