4-Aminopyrimidine is a nitrogen-containing heteroaromatic compound in which an amino group is substituted at the 4-position of the pyrimidine ring. Its molecular formula is C4H5N3, with a molecular weight of approximately 95.10 g/mol. The pyrimidine core is a six-membered aromatic ring with nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3, which contributes to electron deficiency and allows for a variety of nucleophilic and electrophilic reactions. The amino group at position 4 introduces nucleophilicity and hydrogen-bonding capability, enhancing the chemical and biological reactivity of the molecule.
Synthesis of 4-aminopyrimidine is typically achieved through condensation of β-dicarbonyl compounds with guanidine derivatives under controlled conditions to form the pyrimidine ring. Alternative methods include nucleophilic substitution on halopyrimidines with ammonia or amines to introduce the 4-amino group. Reaction conditions are optimized to ensure regioselective substitution and to minimize side reactions such as polyalkylation or degradation of the heterocycle.
Chemically, 4-aminopyrimidine exhibits reactivity at both the amino group and the pyrimidine ring. The amino group can undergo acylation, alkylation, and condensation reactions to form amides, Schiff bases, or other nitrogen-containing derivatives. The pyrimidine ring can participate in electrophilic substitution at activated positions and serves as a scaffold for further functionalization, including halogenation, nitration, and cross-coupling reactions. The electron-deficient nature of the ring influences the regioselectivity and reactivity of these transformations.
4-Aminopyrimidine is generally a crystalline solid at room temperature and exhibits good solubility in polar organic solvents such as water, ethanol, and dimethyl sulfoxide. It is stable under neutral conditions but may be sensitive to strong acids or oxidizing agents, which can modify the amino group or degrade the heterocyclic ring. Its ability to form hydrogen bonds and participate in π–π interactions affects solubility, crystallization, and intermolecular behavior.
In practical applications, 4-aminopyrimidine is widely used as a building block in medicinal chemistry, agrochemical synthesis, and heterocyclic chemistry. Its amino and pyrimidine functionalities enable the construction of functionalized pyrimidine derivatives, kinase inhibitors, and nucleobase analogues. The compound serves as a versatile intermediate for the design and optimization of bioactive molecules, allowing systematic exploration of structure–activity relationships and the development of novel pharmaceuticals.
Overall, 4-aminopyrimidine combines a nucleophilic amino group with an electron-deficient heteroaromatic ring, making it a valuable intermediate in synthetic chemistry. Its predictable reactivity, solubility, and structural versatility enable selective functionalization and the synthesis of diverse nitrogen-containing compounds for chemical, biological, and pharmaceutical applications.
References
2023. Synthesis of Spiro(pyrrol-2,5'-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine)-2',4',5,6'-tetraones by the Reaction of Pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4]oxazinetriones with 6-Aminopyrimidine-2,4-diones. Russian Journal of Organic Chemistry.
DOI: 10.1134/s1070428023020033
|



















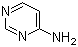
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details