Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Shanghai Worldyang Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13651600618 +86 (21) 5679-5779 | |||
 |
sales7777@worldyachem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: 13651600618 | |||
 |
WhatsApp: +86 13651600618 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink premium supplier since 2023 | ||||
| Hangzhou Verychem Science And Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8816-2785 +86 13606544505 | |||
 |
lucy@verychem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2004 | ||||
| chemBlink massive supplier since 2021 | ||||
| Classification | API >> Antipyretic analgesics >> Antipyretic and analgesic |
|---|---|
| Name | Salicylamide |
| Synonyms | 2-Hydroxybenzamide; o-Hydroxybenzamide |
| Molecular Structure | 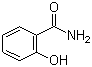 |
| Molecular Formula | C7H7NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 137.14 |
| CAS Registry Number | 65-45-2 |
| EC Number | 200-609-3 |
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C(=C1)C(=O)N)O |
| Water solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL at 20 ºC |
|---|---|
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3, Calc.* |
| Melting point | 140-144 ºC (Expl.) |
| Index of Refraction | 1.612, Calc.* |
| Boiling Point | 318.3±25.0 ºC (760 mmHg), Calc.*, 181 ºC (14 mmHg) (Expl.) |
| Flash Point | 146.3±23.2 ºC, Calc.* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H312-H315-H319-H335 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P264-P264+P265-P270-P271-P280-P301+P317-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P317-P319-P321-P330-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P403+P233-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Salicylamide is an organic compound with the chemical formula C7H7NO2. It is a white crystalline solid that is used in a variety of industrial, pharmaceutical, and laboratory applications. Salicylamide is a derivative of salicylic acid and is closely related to aspirin, a common analgesic. Its chemical structure includes a hydroxyl group (–OH) and an amide group (–NH2) attached to a benzene ring, which gives it its distinctive properties and reactivity. The discovery of salicylamide dates back to the late 19th century when it was first synthesized as a derivative of salicylic acid. The compound's structure was identified through early organic synthesis techniques that focused on modifying phenolic compounds. Researchers sought to create a substance with properties similar to salicylic acid, but with an improved safety and efficacy profile for therapeutic use. Salicylamide was one of the compounds identified during this period as part of the exploration of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Salicylamide has a variety of applications, particularly in the pharmaceutical industry. One of its primary uses is as an analgesic and antipyretic, similar to aspirin. It is sometimes included in formulations for the treatment of mild to moderate pain, such as headaches, muscle aches, and dental pain. Its action is similar to other NSAIDs, working by inhibiting enzymes that produce prostaglandins—chemicals involved in the body's inflammatory response. By blocking the formation of prostaglandins, salicylamide reduces pain and fever. Salicylamide is also used in the treatment of minor muscle and joint pain. Topical formulations, such as creams or gels, often contain salicylamide, which can be applied directly to the skin for localized pain relief. The compound’s anti-inflammatory properties are particularly useful in these formulations, as they help reduce swelling and discomfort caused by conditions such as arthritis or muscle strain. In addition to its use in pain management, salicylamide has applications in the field of laboratory chemistry. It is utilized as a reagent in various organic synthesis reactions. The compound's ability to undergo further chemical modifications makes it valuable for researchers working on the synthesis of other biologically active molecules. Its stability and reactivity make it an ideal candidate for use in the preparation of other pharmaceutical intermediates. Salicylamide is also used in the synthesis of azo dyes, particularly in the textile industry. It can be chemically modified to produce compounds that serve as colorants for fabrics and materials. The compound's versatility in organic chemistry has made it an essential intermediate in the development of other functionalized aromatic compounds that can be used in a range of industrial applications. Despite its many beneficial uses, salicylamide must be handled with care due to potential side effects and toxicity. Like other NSAIDs, it can cause gastrointestinal irritation, and long-term use may lead to kidney or liver damage. It is important for individuals to follow dosing recommendations when using salicylamide-containing products to avoid adverse reactions. Additionally, individuals with certain health conditions, such as ulcers or bleeding disorders, should avoid its use unless directed by a healthcare provider. In conclusion, salicylamide is a versatile compound with applications in pain management, topical treatments, organic synthesis, and industrial processes such as dye production. Its ability to reduce pain and inflammation, combined with its stability and reactivity, makes it an important substance in both therapeutic and industrial settings. Continued research into its uses may lead to new formulations and applications, particularly in the pharmaceutical industry. References 1954. Enzymatic Conversion of Salicylhydroxamic Acid to Salicylamide. Nature, 174(4418). DOI: 10.1038/174036a0 1986. Availability of plasma sulfate for conjugation of salicylamide in dogs. Biochemical Pharmacology, 35(4). DOI: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90235-2 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Salicylamide |