Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Shanghai Worldyang Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13651600618 +86 (21) 5679-5779 | |||
 |
sales7777@worldyachem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: 13651600618 | |||
 |
WhatsApp: +86 13651600618 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink premium supplier since 2023 | ||||
| Classification | Chemical reagent >> Organic reagent >> Amide |
|---|---|
| Name | 5-(4-Formyl-2-methoxyphenoxy)-2-pyrazinecarboxamide |
| Molecular Structure | 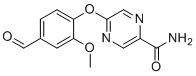 |
| Molecular Formula | C13H11N3O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 273.24 |
| CAS Registry Number | 676500-66-6 |
| SMILES | COc1cc(C=O)ccc1Oc1cnc(C(N)=O)cn1 |
|
5-(4-Formyl-2-methoxyphenoxy)-2-pyrazinecarboxamide is a synthetic aromatic heterocyclic compound consisting of a pyrazinecarboxamide core substituted at the 5-position by a 4-formyl-2-methoxyphenoxy group. This molecule integrates several functional moieties of interest in medicinal and synthetic chemistry, including an aldehyde, a methoxyphenyl ether, and a pyrazine ring system. The central pyrazine ring is a six-membered heterocycle containing two nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 4, known for its aromatic stability and its utility in biologically active molecules. Substituted pyrazinecarboxamides are structurally versatile scaffolds found in a variety of drug candidates, including antimicrobial, anticancer, and anti-inflammatory agents. In this compound, the carboxamide group at the 2-position contributes hydrogen-bonding capacity and increases molecular polarity, which can affect solubility and interaction with biological targets. The phenoxy substituent at the 5-position is functionalized with a methoxy group at the 2-position and an aldehyde group at the 4-position. The methoxy group serves as an electron-donating substituent that can influence the electronic distribution of the aromatic system, potentially affecting reactivity and binding interactions. The formyl group at the 4-position is an electrophilic site that can undergo condensation reactions with amines or hydrazines, making the molecule a potential intermediate in further derivatization or library synthesis for drug discovery applications. Although no specific pharmaceutical product based on 5-(4-formyl-2-methoxyphenoxy)-2-pyrazinecarboxamide is currently approved, derivatives containing similar motifs have been explored in the development of enzyme inhibitors, receptor modulators, and other bioactive agents. The combination of a substituted phenyl ether and a pyrazinecarboxamide scaffold has been reported in several studies aiming to identify molecules with selective activity against cancer cells or microbial pathogens. Synthetic access to this compound generally involves the formation of the phenoxy linkage via nucleophilic aromatic substitution, followed by selective functional group transformations to introduce the methoxy and formyl groups on the phenyl ring. The pyrazinecarboxamide core is typically prepared from halogenated pyrazine intermediates or by direct functionalization of pyrazine dicarboxylic acid derivatives. The final step may involve amide coupling using carboxylic acid activation or conversion of a nitrile or ester intermediate. This compound, due to its functional group diversity, can serve as a useful intermediate or building block in organic synthesis. The formyl group allows for further transformation into Schiff bases, oximes, or hydrazones, while the amide and methoxy groups may influence bioavailability, metabolic stability, or membrane permeability in a biological context. Additionally, the compound can be analyzed and characterized using standard techniques such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), mass spectrometry (MS), and infrared (IR) spectroscopy. In summary, 5-(4-formyl-2-methoxyphenoxy)-2-pyrazinecarboxamide is a multifunctional heteroaromatic compound containing a pyrazinecarboxamide moiety linked to a substituted phenyl ether. While not currently in clinical use, it exemplifies a class of compounds widely investigated for pharmaceutical and synthetic applications due to its reactive aldehyde, aromatic, and nitrogen-containing structural features. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 5-(4-Formyl-2-methoxyphenoxy)-2-pyrazinecarboxamide |