Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Shanghai Worldyang Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13651600618 +86 (21) 5679-5779 | |||
 |
sales7777@worldyachem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: 13651600618 | |||
 |
WhatsApp: +86 13651600618 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink premium supplier since 2023 | ||||
| Classification | Organic raw materials >> Heterocyclic compound >> Imidazoles |
|---|---|
| Name | 1-Ethylimidazole |
| Synonyms | N-Ethylimidazole |
| Molecular Structure | 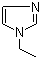 |
| Molecular Formula | C5H8N2 |
| Molecular Weight | 96.13 |
| CAS Registry Number | 7098-07-9 |
| EC Number | 230-403-9 |
| SMILES | CCN1C=CN=C1 |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.*, 0.993 g/mL (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Melting point | -27 ºC (Expl.) |
| Boiling point | 206.9±9.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)*, 224 ºC (Expl.) |
| Flash point | 78.9±18.7 ºC (Calc.)*, 91.5 ºC (Expl.) |
| Index of refraction | 1.517 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |

 GHS05;GHS07 Danger Details
GHS05;GHS07 Danger Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H318-H412 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P264-P264+P265-P270-P273-P280-P301+P317-P302+P352-P305+P354+P338-P317-P321-P330-P332+P317-P362+P364-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
1-Ethylimidazole is a nitrogen-containing heterocyclic organic compound belonging to the imidazole family. Its molecular formula is C5H8N2, and its structure consists of an imidazole ring substituted at the nitrogen atom (position 1) with an ethyl group. The compound is a clear, colorless to pale yellow liquid at room temperature and is soluble in water and various organic solvents due to its polar nature. 1-Ethylimidazole is synthesized through the alkylation of imidazole using ethyl halides such as ethyl bromide or ethyl iodide. The reaction typically proceeds under basic conditions, often in the presence of a solvent like acetonitrile or dimethylformamide, and a base such as potassium carbonate or sodium hydride. The nucleophilic nitrogen atom at position 1 of the imidazole ring attacks the electrophilic carbon of the ethyl halide, leading to N-ethylation. This compound is widely used as a building block in the synthesis of ionic liquids, pharmaceuticals, and coordination compounds. In the field of ionic liquids, 1-ethylimidazole is often used as a precursor for the preparation of 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium-based ionic liquids by further alkylation at the remaining nitrogen. These ionic liquids are employed in electrochemistry, catalysis, separation science, and green chemistry due to their low volatility, high thermal stability, and tunable physicochemical properties. In pharmaceutical research, 1-ethylimidazole serves as an intermediate in the synthesis of drug candidates and biologically active molecules. The imidazole ring is a key pharmacophore in many therapeutic agents due to its ability to participate in hydrogen bonding and coordination to metal centers in enzymes and receptors. The ethyl substituent modifies the electronic properties and lipophilicity of the ring, thereby influencing the pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of the resulting compounds. Coordination chemistry also benefits from 1-ethylimidazole as a ligand in metal complex formation. Its nitrogen atoms can donate electron density to transition metal centers, leading to stable complexes used in catalysis and material science. These complexes can exhibit catalytic activity in oxidation, hydrogenation, and polymerization reactions. Analytical methods used for the characterization of 1-ethylimidazole include nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, which provides detailed information about the chemical environment of protons and carbons in the molecule. Infrared (IR) spectroscopy is employed to confirm the presence of characteristic imidazole ring vibrations. Mass spectrometry (MS) is used to determine molecular weight and fragmentation patterns. Gas chromatography (GC) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) are used to assess purity and concentration in mixtures. 1-Ethylimidazole has moderate volatility and a boiling point around 208 °C. Its density and refractive index are also well-documented, facilitating its identification and use in various applications. Due to its polar structure, it exhibits good solubility in water, alcohols, and polar aprotic solvents. From a safety standpoint, 1-ethylimidazole should be handled with standard laboratory precautions. It may cause irritation to the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract upon exposure. Proper ventilation, protective gloves, and eyewear are recommended during use. In summary, 1-ethylimidazole is a versatile chemical intermediate and ligand known for its role in the synthesis of ionic liquids, pharmaceuticals, and coordination compounds. Its structural features, including the ethyl substitution on the imidazole ring, enhance its reactivity and solubility, making it a valuable component in modern synthetic and materials chemistry. References 2019. Quantification of Imidazole Compounds in Ambient Aerosols at Suburban and Forest Sites in Western Japan. Asian Journal of Atmospheric Environment, 13(4). DOI: 10.5572/ajae.2019.13.4.259 2022. Cobalt(II)-Imidazoles Passivated α-Fe2O3 Photoanode for Enhanced Photoelectrochemical Water Oxidation. Catalysis Letters, 152(1). DOI: 10.1007/s10562-021-03909-w 2022. A Trilaminar-Thermosensitive Hydrogel Catalytic Reactor Capable of Single/Tandem Catalytic Switchable Ability. Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials, 32(12). DOI: 10.1007/s10904-022-02513-8 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 1-Ethylimidazole |