Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| MolScanner | Singapore | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 18621675448 | |||
 |
marketing@molscanner.com | |||
 |
WhatsApp: 9896 7603 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2025 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Classification | Pharmaceutical intermediate >> Heterocyclic compound intermediate >> Pyrimidine compound >> Ketones |
|---|---|
| Name | 5,8-Diamino-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one |
| Molecular Structure | 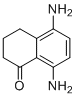 |
| Molecular Formula | C10H12N2O |
| Molecular Weight | 176.22 |
| CAS Registry Number | 746589-05-9 |
| SMILES | C1CC2=C(C=CC(=C2C(=O)C1)N)N |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 417.1±45.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)* |
| Flash point | 206.0±28.7 ºC (Calc.)* |
| Index of refraction | 1.676 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
|
The chemical substance 5,8-diamino-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, a functionalized tetralone derivative with two amino groups, is recognized in organic chemistry as a valuable synthetic intermediate, particularly in pharmaceutical and materials chemistry. Its discovery and applications are well-documented in the literature, rooted in the development of tetralin-based compounds and regioselective amination techniques. The origins of this compound are tied to the study of tetralones, bicyclic molecules comprising a benzene ring fused to a cyclohexanone, which have been explored since the early 20th century for their presence in natural products and utility as synthetic scaffolds. The 3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one core, commonly known as 1-tetralone, gained prominence in the mid-20th century for its reactivity and versatility in medicinal chemistry. The introduction of amino groups at the 5- and 8-positions became feasible with advances in regioselective aromatic substitution and reduction techniques during the 1960s and 1970s. These advancements, driven by the pharmaceutical industry’s demand for polar, multifunctional intermediates, enabled the synthesis of compounds like 5,8-diamino-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one in the late 20th century to serve as building blocks for bioactive molecules. Synthetically, 5,8-diamino-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one is typically prepared through a multi-step process. A common route starts with 1-tetralone, which is nitrated at the 5- and 8-positions using nitric acid under controlled conditions to yield 5,8-dinitro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one. The nitro groups are then reduced to amines using catalytic hydrogenation with palladium on carbon or a chemical reducing agent like tin(II) chloride in hydrochloric acid. Alternatively, the synthesis may involve a protected tetralone precursor, where the ketone is masked as a ketal to facilitate regioselective nitration and reduction, followed by deprotection to restore the carbonyl group. These steps rely on well-established aromatic substitution, reduction, and ketone chemistry protocols, ensuring regioselectivity and high yields. The primary application of 5,8-diamino-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one is as a synthetic intermediate in pharmaceutical chemistry. The tetralone core provides a rigid, partially saturated scaffold that mimics structural features of natural products and enhances binding to biological targets. The 5- and 8-amino groups serve as versatile handles for forming amides, amines, or heterocycles, enabling the construction of complex molecular architectures. This compound is frequently used in the synthesis of drug candidates, including analgesics, anticancer agents, and central nervous system modulators, where the diamino groups contribute to hydrogen-bonding interactions and solubility, and the ketone allows further functionalization, such as reductive amination or aldol reactions. In addition to pharmaceuticals, the compound is employed in materials chemistry for synthesizing dyes, fluorescent probes, or polymers, where the diamino groups facilitate conjugation and the tetralone core provides structural rigidity. In academic research, it serves as a model compound for studying regioselective amination, tetralone reactivity, and the electronic effects of diamino substitution. Its synthesis has contributed to the refinement of nitration and reduction techniques. The significance of 5,8-diamino-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one lies in its role as a multifunctional intermediate that combines the structural versatility of tetralones with the synthetic utility of diamino groups. Its development reflects progress in regioselective functionalization and aromatic chemistry. By enabling the efficient synthesis of complex, biologically active molecules, it has become a critical tool in advancing pharmaceutical, materials, and chemical research. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 5,8-Diamino-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one |