Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Capot Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8558-6718 +86 13336195806 | |||
 |
capotchem@gmail.com sales@capotchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2006 | ||||
| Shanghai Rory Fine Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (21) 5070-2305 | |||
 |
rorychem@hotmail.com 13701863355@139.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2005 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2007 | ||||
| Simagchem Corporation | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13806087780 | |||
 |
sale@simagchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| Tianjin Zhongxin Chem-tech Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (22) 6688-0623 | |||
 |
sales@tjzxchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2007 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2009 | ||||
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (551) 6541-8684 | |||
 |
sales@tnjchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2001 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Dishman Pharmaceuticals & Chemicals Limited | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (732) 560-4300 | |||
 |
bhaveshoza@dishmangroup.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2011 | ||||
| Synthetics China Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (523) 8798-0162 | |||
 |
shirley.tian@synthetics-china.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2012 | ||||
| Anhui Royal Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (25) 8663-9253 | |||
 |
zoey.zhao@royal-chem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2008 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2019 | ||||
| Classification | Organic raw materials >> Amino compound >> Cycloalkylamines, aromatic monoamines, aromatic polyamines and derivatives and salts |
|---|---|
| Name | N-Isopropylaniline |
| Synonyms | N-(1-Methylethyl)benzenamine; N-Phenylisopropylamine; N-IPA |
| Molecular Structure | 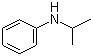 |
| Molecular Formula | C9H13N |
| Molecular Weight | 135.21 |
| CAS Registry Number | 768-52-5 |
| EC Number | 212-196-7 |
| SMILES | CC(C)NC1=CC=CC=C1 |
| Density | 0.934 |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 202 ºC |
| Refractive index | 1.539 |
| Flash point | 87.7 ºC |
| Water solubility | <0.01 g/100 mL at 21 ºC |
| Hazard Symbols |

 GHS06;GHS07 Danger Details
GHS06;GHS07 Danger Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H330-H335 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P260-P261-P264-P264+P265-P270-P271-P273-P280-P284-P301+P317-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P316-P319-P320-P321-P330-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P403+P233-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transport Information | UN 2810 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
N-Isopropylaniline, an organic compound with the molecular formula C₉H₁₃N, belongs to the class of secondary amines. It is characterized by the presence of an isopropyl group attached to the nitrogen atom of an aniline structure. The compound was first synthesized in the late 19th century as chemists began exploring the properties and reactions of amines and their derivatives. Its structural features allow it to participate in a variety of chemical reactions, leading to numerous applications in various industries. The synthesis of N-isopropylaniline typically involves the alkylation of aniline with isopropyl halides or through the reductive amination of acetophenone using isopropylamine. This straightforward synthetic route has made N-isopropylaniline readily available for research and industrial purposes. Its unique properties, including the ability to act as a nucleophile due to the electron-donating effect of the isopropyl group, make it a valuable intermediate in organic synthesis. One of the primary applications of N-isopropylaniline is in the production of dyes and pigments. It serves as a key building block in the synthesis of various azo dyes, which are widely used in textiles, food, and cosmetics due to their vibrant colors and stability. The electron-donating properties of the isopropyl group enhance the dyeing performance, making N-isopropylaniline a crucial component in the dye industry. In addition to its role in dye manufacturing, N-isopropylaniline is also utilized in the formulation of agricultural chemicals, particularly in the synthesis of herbicides and pesticides. Its reactivity enables the formation of various herbicidal agents, contributing to the development of effective crop protection strategies. The compound’s ability to enhance the bioavailability and effectiveness of these chemicals has made it an essential part of agrochemical formulations. Furthermore, N-isopropylaniline finds application in the production of pharmaceuticals and fine chemicals. It serves as a precursor for the synthesis of various biologically active compounds, including pharmaceuticals and therapeutic agents. The compound's versatility in organic synthesis makes it a valuable intermediate in the pharmaceutical industry, aiding in the development of new drugs and treatments. Despite its useful applications, N-isopropylaniline must be handled with care due to potential health risks associated with exposure. It is classified as harmful if inhaled, ingested, or if it comes into contact with skin. Proper safety precautions should be implemented during its use in industrial and laboratory settings to mitigate any associated hazards. In summary, N-isopropylaniline is an important organic compound with a range of applications across various industries, including dye production, agriculture, and pharmaceuticals. Its discovery and subsequent utilization have contributed significantly to advancements in organic synthesis and chemical manufacturing, highlighting its role as a valuable building block in modern chemistry. References 2024. Synthesis of N- and C-terpenylanilines and the study of their properties. Russian Chemical Bulletin, 73(3). DOI: 10.1007/s11172-024-4168-z 2024. Nickel-catalyzed enantioselective reductive amination of benzylic ketones in alcohols. Science China Chemistry, 67(7). DOI: 10.1007/s11426-024-2019-1 2020. Green H2O-Promoted Solvent-Free Synthesis of Enaminocarbonyl Compounds with High Stereoselectivity from Electron-Deficient Terminal Alkynes. Synlett, 31(8). DOI: 10.1055/s-0040-1707968 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for N-Isopropylaniline |