Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Chemfun Medical Technology (shanghai) Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (21) 6722-0633 | |||
 |
sales1@chemfun.net | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: 3046659337 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2010 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Classification | Organic raw materials >> Carboxylic compounds and derivatives >> Carboxylic esters and their derivatives |
|---|---|
| Name | Succinimidyl tert-butyl hexadecandioate |
| Synonyms | 1-O-tert-butyl 16-O-(2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl) hexadecanedioate |
| Molecular Structure | 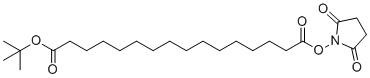 |
| Molecular Formula | C24H41NO6 |
| Molecular Weight | 439.59 |
| CAS Registry Number | 843666-28-4 |
| SMILES | CC(C)(C)OC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)ON1C(=O)CCC1=O |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 514.1±42.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)* |
| Flash point | 264.7±27.9 ºC (Calc.)* |
| Index of refraction | 1.492 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| SDS | Available |
|---|---|
|
Succinimidyl tert-butyl hexadecandioate is a diester derivative of hexadecanedioic acid in which one carboxyl group is protected as a tert-butyl ester and the other is activated as an N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) ester. This combination of functional groups makes the molecule highly useful as a bifunctional reagent in organic synthesis, bioconjugation, and polymer chemistry. The compound can be synthesized through sequential esterification and activation reactions. First, one carboxyl group of hexadecanedioic acid is selectively protected as a tert-butyl ester using standard acid-catalyzed esterification conditions. The remaining free carboxyl group is then converted into the NHS ester using N-hydroxysuccinimide in the presence of a coupling agent such as dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC). This strategy yields a molecule that is stable under neutral and basic conditions but reactive toward nucleophiles such as amines. Succinimidyl tert-butyl hexadecandioate is primarily applied as a cross-linking agent in peptide and protein chemistry. The NHS ester reacts readily with primary amines to form stable amide bonds, while the tert-butyl-protected carboxyl group can later be deprotected under acidic conditions to reveal a free carboxyl for further functionalization. This property allows for controlled stepwise conjugation, which is essential in designing multifunctional biomolecules, polymers, or drug-delivery vehicles. In polymer chemistry, this bifunctional reagent can be used to introduce long-chain linkers with selective reactivity. The hexadecandioate chain provides hydrophobic spacing and flexibility, which can influence polymer properties such as solubility, crystallinity, and mechanical strength. The selective activation of one end as an NHS ester enables precise attachment to amine-functionalized substrates, supporting the creation of well-defined macromolecular architectures. In medicinal chemistry, molecules derived from succinimidyl tert-butyl hexadecandioate have been used to attach hydrophobic moieties to peptides or proteins, which can improve membrane permeability, modulate pharmacokinetics, or enable targeted drug delivery. Its bifunctional nature facilitates the incorporation of both reactive and protective elements, allowing for iterative synthetic strategies and modular assembly of complex molecules. Physically, succinimidyl tert-butyl hexadecandioate is typically a solid at room temperature, with moderate solubility in organic solvents such as dichloromethane, dimethylformamide, or tetrahydrofuran. The compound is sensitive to moisture, as hydrolysis of the NHS ester leads to loss of reactivity. Storage under anhydrous conditions and at low temperature is recommended to preserve its chemical stability. Overall, succinimidyl tert-butyl hexadecandioate is a valuable synthetic reagent due to its dual functionality: a protected carboxyl group for later modification and an activated NHS ester for rapid and selective amide bond formation. This combination makes it highly useful in the preparation of bioconjugates, functional polymers, and complex organic molecules, providing controlled reactivity and versatility for research and industrial applications. References 2021. Fatty acid modified human epidermal growth factor. WO Patent. URL: WO-2019023295-A1 2017. HUMAN EPIDERMAL GROWTH FACTOR MODIFIED BY FATTY ACID. US Patent. URL: US-2020190157-A1 2008. Protease stabilized, acylated insulin analogues. EP Patent. URL: EP-2254906-B1 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Succinimidyl tert-butyl hexadecandioate |