Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Simagchem Corporation | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13806087780 | |||
 |
sale@simagchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| Topscience Co. Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (400) 820-0310 | |||
 |
sales@tsbiochem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2013 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2012 | ||||
| Hangzhou Leap Chem Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8771-1850 | |||
 |
market19@leapchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2006 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Aaron Chemistry GmbH | Germany | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+49 (8823) 917-521 | |||
 |
sales@aaron-chemistry.de | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| Trans World Chemicals, Inc. | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (301) 279-2295 | |||
 |
info@transworldchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1974 | ||||
| Hubei Organic And Phosphoric Chemicals Import & Export Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (27) 8579-6109 8577-2811 | |||
 |
sales@hubeichem.com | |||
| Chemical distributor | ||||
| Classification | Organic raw materials >> Aryl compounds >> Anilines |
|---|---|
| Name | 3-Methylbenzylamine |
| Synonyms | m-Xylylamine |
| Molecular Structure | 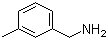 |
| Molecular Formula | C8H11N |
| Molecular Weight | 121.18 |
| CAS Registry Number | 100-81-2 |
| EC Number | 202-890-8 |
| SMILES | CC1=CC(=CC=C1)CN |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 200.2±9.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)*, 202 - 205 ºC (Expl.) |
| Flash point | 80.6 ºC (Calc.)*, 80 ºC (Expl.) |
| Index of refraction | 1.542 (Calc.)*, 1.536 (Expl.) |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS05 Danger Details
GHS05 Danger Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H314 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P260-P264-P280-P301+P330+P331-P302+P361+P354-P304+P340-P305+P354+P338-P316-P321-P363-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transport Information | UN 2735 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
3-Methylbenzylamine, also known as m-tolylmethylamine, is an organic compound belonging to the class of aromatic amines. It is characterized by a methyl group substituted at the meta position of the benzene ring relative to a benzylamine moiety. The molecular formula of 3-methylbenzylamine is C8H11N, and its structure consists of a benzene ring with a methyl substituent at the 3-position and a -CH2NH2 group attached to the ring. This compound appears as a colorless to pale yellow liquid and has a characteristic amine-like odor. The synthesis of 3-methylbenzylamine has been reported in the literature through several established methods. A common approach involves the reductive amination of 3-methylbenzaldehyde using ammonia or a primary amine in the presence of a reducing agent such as hydrogen over a metal catalyst or sodium cyanoborohydride. Another method includes the reduction of 3-methylbenzonitrile or 3-methylbenzyl azide to the corresponding amine. These routes have been extensively studied and optimized for laboratory and industrial applications, offering good yields and functional group tolerance. 3-Methylbenzylamine has been used as a versatile building block and intermediate in organic synthesis. Its amine functionality allows it to participate in various types of reactions, such as acylation, alkylation, sulfonylation, and Schiff base formation. One of the main areas of application is in the synthesis of pharmaceutical compounds, where it serves as a precursor for drug candidates and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). The amine group of 3-methylbenzylamine can be modified to introduce pharmacologically active moieties, and the methyl substitution on the aromatic ring may influence the biological activity and metabolic stability of the derived compounds. In agrochemical research, 3-methylbenzylamine has also been employed in the synthesis of herbicides and insecticides. It contributes to the design of active molecules with improved potency and selectivity through structural modifications. Derivatives of 3-methylbenzylamine have been tested for activity in various bioassays targeting specific pests and plant diseases. In polymer chemistry, 3-methylbenzylamine can be used as a curing agent or modifier for epoxy resins and polyurethanes. The primary amine group reacts with epoxide or isocyanate groups, facilitating the formation of cross-linked polymer networks. The presence of the methyl group on the aromatic ring can influence the rigidity and thermal properties of the resulting polymer materials. Additionally, 3-methylbenzylamine has been utilized in coordination chemistry as a ligand precursor. By reacting with metal salts, it can form coordination complexes that are of interest in catalysis and materials science. The steric and electronic properties of the 3-methylbenzyl group can affect the binding mode and stability of such complexes. Safety data indicate that 3-methylbenzylamine should be handled with care, as it may cause irritation to the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract. Standard precautions are necessary when working with this compound in both laboratory and industrial settings. It is recommended to use personal protective equipment and operate under appropriate ventilation conditions. In summary, 3-methylbenzylamine is a valuable compound in synthetic organic chemistry, with established uses in the pharmaceutical, agrochemical, polymer, and coordination chemistry fields. Its chemical properties and reactivity make it a useful intermediate for the development of a wide range of functional materials and bioactive molecules. References 1988. Conformational and steric aspects of the inhibition of phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase by benzylamines. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 31(2). DOI: 10.1021/jm00397a029 1999. Charge-Assisted Hydrogen Bonds and Halogen-Halogen Interactions in Organic Salts: Benzylammonium Benzoates and Pentafluorobenzoates. Structural Chemistry, 10(3). DOI: 10.1023/a:1021892631355 2022. Assembly of two new hybrid chloride materials with potential NLO properties: Structure elucidation, empirical and computational studies. Journal of the Iranian Chemical Society, 19(5). DOI: 10.1007/s13738-021-02469-5 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 3-Methylbenzylamine |