Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Chemmltech Pharmaceuticals Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+852 6362-1062 | |||
 |
admin@chemmltech.com | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2024 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Classification | Organic raw materials >> Amino compound >> Amide compound |
|---|---|
| Name | EPI-589 |
| Synonyms | (2R)-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-4-(2,4,5-trimethyl-3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-dien-1-yl)butanamide |
| Molecular Structure | 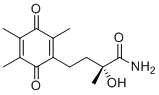 |
| Molecular Formula | C14H19NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 265.30 |
| CAS Registry Number | 1147883-03-1 |
| SMILES | CC1=C(C(=O)C(=C(C1=O)C)CC[C@](C)(C(=O)N)O)C |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 465.0±45.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)* |
| Flash point | 235.0±28.7 ºC (Calc.)* |
| Index of refraction | 1.535 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| SDS | Available |
|---|---|
|
EPI-589, also known as vatiquinone or α-tocopheryloxyacetic acid quinone, is a redox-active small molecule under investigation primarily for its potential neuroprotective effects in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. It is a synthetic quinone derivative structurally related to vitamin E analogs and has been developed to target oxidative stress pathways implicated in mitochondrial dysfunction and neuronal cell death. The compound has gained particular attention for its potential role in treating amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and other disorders involving mitochondrial impairment. The discovery of EPI-589 arose from efforts to improve upon naturally occurring antioxidant molecules by enhancing their redox cycling efficiency and cellular uptake. Unlike standard antioxidants, EPI-589 is capable of undergoing intracellular redox cycling to scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS) while also helping to maintain mitochondrial function. The structure of EPI-589 allows it to be reduced inside cells to its active hydroquinone form, which can then interact with oxidative stress mediators and potentially protect cells from damage. The compound was originally synthesized by researchers seeking to develop therapeutic agents for mitochondrial diseases and oxidative stress-related conditions. Its design was influenced by the need to improve bioavailability and redox potential over earlier vitamin E derivatives. In preclinical studies, EPI-589 showed protective effects in models of oxidative injury, and its reduced form demonstrated the ability to modulate redox balance and mitochondrial homeostasis. In terms of application, EPI-589 has been most extensively studied for its potential in ALS, a fatal neurodegenerative disorder characterized by progressive loss of motor neurons. In preclinical models, EPI-589 improved mitochondrial function and reduced neuronal degeneration, prompting early-stage clinical development. It has also been explored for its effects in other disorders linked to mitochondrial dysfunction, such as Leigh syndrome and Parkinson’s disease. These applications are based on the compound’s ability to regulate intracellular redox status and modulate mitochondrial bioenergetics. EPI-589 is administered orally and is considered to have favorable pharmacokinetic properties, including good absorption and distribution in target tissues. Studies in animal models have shown that it crosses the blood-brain barrier, a key requirement for any compound targeting neurodegenerative conditions. Safety evaluations have indicated a generally favorable profile, although comprehensive clinical data are still limited due to the ongoing nature of trials. Mechanistically, the drug acts as a catalytic antioxidant, unlike traditional antioxidants that are consumed in the process of neutralizing ROS. This means that EPI-589 can exert sustained antioxidant effects through redox cycling without being depleted, enhancing its potential therapeutic value. In vitro and in vivo studies have also shown that EPI-589 can reduce markers of lipid peroxidation and protect neurons from glutathione depletion-induced toxicity, both of which are critical aspects of oxidative damage in neurodegenerative diseases. While not yet approved for any indication, EPI-589 continues to be studied in clinical trials, particularly in Japan and the United States, where researchers aim to confirm its efficacy and safety in treating ALS and other mitochondrial diseases. The results of these studies will determine whether it advances to broader clinical use. EPI-589 represents a rationally designed molecule aimed at addressing mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress, which are central to many forms of neurodegeneration. Its development reflects a broader strategy in drug discovery to design redox-active compounds that mimic or enhance the body's natural defense mechanisms, potentially offering new avenues for the treatment of otherwise intractable neurological disorders. References 2022. Phase 1 Study to Investigate the Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of EPI-589 in Healthy Participants. Clinical Pharmacology in Drug Development, 11(10). DOI: 10.1002/cpdd.1146 2023. An Exploratory Trial of EPI-589 in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (EPIC-ALS): Protocol for a Multicenter, Open-Labeled, 24-Week, Single-Group Study. JMIR Research Protocols, 12. DOI: 10.2196/42032 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for EPI-589 |