Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Guangzhou Green Cross Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (20) 8222-0238 | |||
 |
wangsy@m-pharma.com.cn | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1991 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2024 | ||||
| Classification | API >> Antibiotics >> Peptide drug |
|---|---|
| Name | Dotinurad |
| Synonyms | (3,5-dichloro-4-hydroxyphenyl)-(1,1-dioxo-2H-1,3-benzothiazol-3-yl)methanone |
| Molecular Structure | 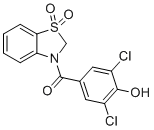 |
| Molecular Formula | C14H9Cl2NO4S |
| Molecular Weight | 358.20 |
| CAS Registry Number | 1285572-51-1 |
| SMILES | C1N(C2=CC=CC=C2S1(=O)=O)C(=O)C3=CC(=C(C(=C3)Cl)O)Cl |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 614.8±55.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)* |
| Flash point | 325.6±31.5 ºC (Calc.)* |
| Index of refraction | 1.693 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details |
|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319 Details |
| Precautionary Statements | P264-P280-P302+P352-P337+P313-P305+P351+P338-P362+P364-P332+P313 Details |
| SDS | Available |
|
Dotinurad is a uricosuric agent developed for the treatment of hyperuricemia, including gout, by promoting the excretion of uric acid through the kidneys. It functions as a selective inhibitor of urate transporter 1 (URAT1), a transporter protein located on the apical membrane of renal proximal tubular cells that is primarily responsible for the reabsorption of uric acid from urine back into the bloodstream. By inhibiting URAT1, dotinurad reduces serum uric acid levels and increases urinary uric acid excretion, thereby addressing the underlying cause of hyperuricemia in many patients. The development of dotinurad was part of a broader effort to create uricosuric drugs with improved safety and selectivity. Traditional uricosuric agents such as probenecid and benzbromarone, while effective, have been associated with various limitations, including drug interactions, hepatotoxicity, and reduced efficacy in patients with renal impairment. Dotinurad was synthesized by Fuji Yakuhin Co., Ltd. (Japan), with the goal of creating a URAT1-selective agent with a lower risk of adverse effects and a better safety profile. Dotinurad was approved for clinical use in Japan in 2020 for the treatment of hyperuricemia with or without gout. Its introduction marked a significant development in the therapeutic landscape for uric acid-lowering agents. Clinical trials demonstrated that dotinurad effectively lowers serum uric acid levels in a dose-dependent manner, with efficacy comparable to existing therapies. Importantly, it maintained a favorable safety profile, with fewer hepatic adverse effects and a lower risk of renal calculi compared to some earlier uricosuric agents. Pharmacologically, dotinurad is administered orally and exhibits good bioavailability. It is rapidly absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract and reaches peak plasma concentration within a few hours. Its half-life and pharmacokinetics support once-daily dosing, which enhances patient adherence. Dotinurad is metabolized primarily in the liver and excreted in both urine and feces. The drug’s selectivity for URAT1, with minimal effects on other renal transporters such as glucose or organic anion transporters, contributes to its specificity and reduced side-effect profile. One of the key advantages of dotinurad is its potential suitability for a broader range of patients, including those with mild to moderate renal dysfunction. Unlike some other uricosurics whose effectiveness diminishes with impaired renal function, dotinurad has shown consistent urate-lowering activity across varying degrees of renal performance, although caution is still advised in patients with significant renal impairment. Dotinurad is not currently approved outside of Japan, and global regulatory pathways are still under evaluation. However, interest in the drug remains high due to its targeted mechanism and promising clinical profile. Post-marketing surveillance in Japan continues to provide data on its long-term safety and effectiveness in real-world use. In addition to its role in treating gout and hyperuricemia, dotinurad has been studied for potential benefits in patients with asymptomatic hyperuricemia, especially those with comorbidities such as hypertension, chronic kidney disease, and metabolic syndrome, where uric acid management may contribute to broader disease control. However, such uses must be carefully evaluated in clinical settings and are not part of its current formal indications. In summary, dotinurad is a novel, selective URAT1 inhibitor developed for the treatment of hyperuricemia and gout. It represents a newer generation of uricosuric drugs, offering improved safety, renal tolerability, and once-daily oral dosing. Its development and approval have contributed to expanding therapeutic options for managing elevated uric acid levels in clinical practice. References 2019. Pharmacological Evaluation of Dotinurad, a Selective Urate Reabsorption Inhibitor. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 371(1). DOI: 10.1124/jpet.119.259341 2024. Current updates and future perspectives in uric acid research, 2024. Hypertension Research, 47(12). DOI: 10.1038/s41440-024-02031-9 2024. Unique Binding Sites of Uricosuric Agent Dotinurad for Selective Inhibition of Renal Uric Acid Reabsorptive Transporter URAT1. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 389(3). DOI: 10.1124/jpet.124.002096 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Dotinurad |