Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Jiangsu Nengyue New Material Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13376001577 | |||
 |
robin@jiangsunengyue.com | |||
 |
WhatsApp: +8613376001577 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2022 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2024 | ||||
| Classification | Organic raw materials >> Organoboron compounds |
|---|---|
| Name | Bis(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)iodonium tetraphenylborate |
| Molecular Structure | 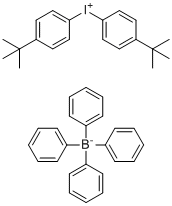 |
| Molecular Formula | C44H46BI |
| Molecular Weight | 712.55 |
| CAS Registry Number | 131725-16-1 |
| EC Number | 685-279-2 |
| SMILES | C1=CC(=CC=C1[I+]C2=CC=C(C=C2)C(C)(C)C)C(C)(C)C.C3=CC=C(C=C3)[B-](C4=CC=CC=C4)(C5=CC=CC=C5)C6=CC=CC=C6 |
| Hazard Symbols |


 GHS05;GHS06;GHS08 Danger Details
GHS05;GHS06;GHS08 Danger Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H301-H314-H335-H360 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P264-P270-P271-P280-P301+P310+P330-P302+P352-P304+P340+P312-P305+P351+P338-P332+P313-P337+P313-P403+P233-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transport Information | UN 2923 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Bis(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)iodonium tetraphenylborate is a prominent iodonium salt utilized as a photoinitiator in various polymerization reactions. Iodonium salts, particularly those with bulky phenyl groups, have long been known for their efficacy in generating reactive species upon exposure to ultraviolet (UV) or visible light. The discovery of Bis(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)iodonium tetraphenylborate capitalized on the stability and reactivity of the iodonium cation paired with the non-nucleophilic tetraphenylborate anion, resulting in a versatile photoinitiator suitable for various industrial applications. The role of the iodonium cation in this compound is to undergo photo-induced homolytic cleavage, producing reactive intermediates that initiate polymerization. Upon light exposure, the bond between iodine and the phenyl group breaks, generating a phenyl radical and a reactive iodonium species. This initiates cationic or free-radical polymerization, depending on the system. The presence of the bulky tert-butyl groups on the phenyl rings stabilizes the iodonium cation and enhances the compound's solubility in organic solvents, broadening its applicability across different formulations. The tetraphenylborate anion contributes significantly to the overall performance of the photoinitiator. This large, weakly coordinating anion ensures the iodonium cation remains highly reactive without interfering with the polymerization process. Additionally, tetraphenylborate is chosen for its excellent solubility in non-polar solvents, allowing Bis(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)iodonium tetraphenylborate to be used in diverse industrial applications where solvent compatibility is crucial. This compound is widely applied in UV-curable coatings, adhesives, and inks due to its ability to efficiently initiate polymerization upon light exposure. In UV-curing technologies, fast setting times and controlled polymerization are critical, making iodonium salts ideal photoinitiators. Bis(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)iodonium tetraphenylborate excels in this role by providing high reactivity and good solubility in typical monomer systems used in the coatings industry. The use of UV-curable coatings is particularly prevalent in automotive finishes, electronics, and packaging, where quick processing times and durable finishes are essential. In addition to coatings, this compound is also employed in the production of photoresists, essential materials in the microelectronics industry. Photoresists are light-sensitive materials used to transfer intricate patterns onto semiconductor substrates. The photoinitiating properties of Bis(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)iodonium tetraphenylborate make it suitable for creating high-resolution patterns in these applications, which are vital for the manufacturing of integrated circuits and other electronic devices. The biomedical field also benefits from this compound's application. UV-cured dental resins and other medical-grade polymers that require biocompatibility and rapid curing use this iodonium salt as a photoinitiator. Its efficiency in initiating polymerization ensures strong bonding and long-lasting performance in dental fillings and coatings. The synthesis of Bis(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)iodonium tetraphenylborate typically involves the reaction of iodophenyl precursors with tert-butylphenyl derivatives, followed by salt metathesis with sodium tetraphenylborate. The reaction conditions are carefully controlled to ensure the formation of a stable iodonium salt with optimal photoinitiating properties. After synthesis, the compound is purified and tested for its photoinitiation efficiency, particularly in UV-curable systems. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Bis(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)iodonium tetraphenylborate |