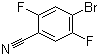
4-Bromo-2,5-difluorobenzonitrile is an organic compound consisting of a benzene ring with three substituent groups: a bromine atom at the 4-position, and two fluorine atoms at the 2- and 5-positions, along with a nitrile group (-CN) at the 1-position. This structure places the compound in the category of halogenated benzonitriles, which are important intermediates in organic synthesis and materials science due to their reactivity and functional properties.
The synthesis of 4-bromo-2,5-difluorobenzonitrile typically involves halogenation reactions, where bromine and fluorine atoms are selectively introduced to the aromatic ring. Bromine can be introduced via electrophilic substitution reactions, often using brominating agents such as NBS (N-bromosuccinimide) or elemental bromine under controlled conditions. The fluorine atoms can be introduced through fluorination reactions, which may involve the use of reagents such as N-fluorobenzenesulfonimide (NFSI), potassium fluoride (KF), or other fluorinating agents to direct the fluorine atoms to the desired positions on the benzene ring.
4-Bromo-2,5-difluorobenzonitrile is of interest for its potential applications in the development of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials science. The nitrile group (-CN) attached to the benzene ring makes it a useful precursor for the synthesis of other organic compounds, as it can undergo various chemical reactions such as nucleophilic addition, reduction, and substitution. The halogen atoms, especially fluorine, can alter the electronic properties of the molecule, influencing its reactivity and making it a useful building block in the design of more complex molecules.
In medicinal chemistry, halogenated benzonitriles like 4-bromo-2,5-difluorobenzonitrile are studied for their ability to interact with biological systems. The presence of fluorine atoms can increase the metabolic stability of a compound, making it less susceptible to enzymatic degradation, while bromine can enhance the compound’s lipophilicity, improving its ability to penetrate cell membranes. These properties make such compounds candidates for further development as therapeutic agents targeting specific enzymes or receptors.
In materials science, 4-bromo-2,5-difluorobenzonitrile may be used in the design and synthesis of functional materials, such as organic semiconductors or liquid crystal displays (LCDs). The fluorine atoms can improve the compound's stability and performance in electronic devices, while the nitrile group can participate in coordination chemistry, potentially forming complexes with metal ions or other ligands.
The compound may also be of interest in the synthesis of advanced organic materials like polymers or molecular sensors. The combination of halogen and nitrile groups provides opportunities for further chemical modifications that could lead to the development of materials with tailored properties for specific applications in catalysis, electronics, or sensor technology.
In conclusion, 4-bromo-2,5-difluorobenzonitrile is a halogenated aromatic compound that offers several applications in organic synthesis, medicinal chemistry, and materials science. Its functional groups, including the bromine, fluorine, and nitrile groups, make it a versatile intermediate for the preparation of more complex molecules. Further research into its chemical reactivity and biological activity could lead to the development of novel compounds with pharmaceutical or industrial applications.
|









 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details