Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Unichem Company Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (510) 823-28705 | |||
 |
webmaster@unionchems.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2001 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2006 | ||||
| Capot Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8558-6718 +86 13336195806 | |||
 |
capotchem@gmail.com sales@capotchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2006 | ||||
| Simagchem Corporation | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13806087780 | |||
 |
sale@simagchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| Shanghai Lingde Chemical Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (21) 5833-3929 | |||
 |
sales@shldchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (551) 6541-8684 | |||
 |
sales@tnjchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2001 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Wilshire Technologies, Inc. | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (609) 683-1117 | |||
 |
Wilshire-info@evonik.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1997 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| BOC Sciences | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 485-4226 | |||
 |
info@bocsci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Dishman Pharmaceuticals & Chemicals Limited | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (732) 560-4300 | |||
 |
bhaveshoza@dishmangroup.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2011 | ||||
| Classification | Chemical reagent >> Organic reagent >> Phosphine ligand |
|---|---|
| Name | Methyltriphenylphosphonium bromide |
| Synonyms | Methyl(triphenyl)phosphonium bromide |
| Molecular Structure | 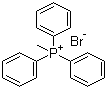 |
| Molecular Formula | C19H18P.Br |
| Molecular Weight | 357.23 |
| CAS Registry Number | 1779-49-3 |
| EC Number | 217-218-9 |
| SMILES | C[P+](C1=CC=CC=C1)(C2=CC=CC=C2)C3=CC=CC=C3.[Br-] |
| Melting point | 230-233 ºC (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Water solubility | 400 g/L (25 ºC) |
| Hazard Symbols |


 GHS06;GHS07;GHS09 Danger Details
GHS06;GHS07;GHS09 Danger Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H300-H301-H302-H312-H315-H319-H332-H411 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P264-P264+P265-P270-P271-P273-P280-P301+P316-P301+P317-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P317-P321-P330-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P391-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Methyltriphenylphosphonium bromide (C6H5)3PCH3Br is a quaternary ammonium salt composed of a methyl group attached to a triphenylphosphonium cation, with a bromide anion. It is typically synthesized by reacting triphenylphosphine with methyl bromide, resulting in the formation of this well-known phosphonium salt. Methyltriphenylphosphonium bromide is widely utilized in organic chemistry, particularly in the Wittig reaction. In this reaction, it reacts with carbonyl compounds such as aldehydes or ketones to generate alkenes. This process involves the formation of a phosphonium ylide intermediate, which facilitates the creation of a carbon-carbon double bond. The Wittig reaction is crucial for the synthesis of a variety of alkenes, which have applications in the pharmaceutical, agrochemical, and material science industries. Apart from its prominent role in the Wittig reaction, methyltriphenylphosphonium bromide is also employed in other synthetic processes involving phosphonium ylides. These ylides can participate in nucleophilic substitution reactions, where they react with electrophilic species to form new carbon-carbon bonds. The reactivity of methyltriphenylphosphonium bromide makes it a useful reagent in various organic synthesis protocols. Methyltriphenylphosphonium bromide is also applied in the preparation of substituted phosphonium salts, which are important intermediates in numerous chemical reactions. Furthermore, it is utilized in the synthesis of other phosphonium compounds that find use in catalysis and other specialized applications in organic chemistry. In conclusion, methyltriphenylphosphonium bromide is a versatile and valuable reagent in organic chemistry. Its key application in the Wittig reaction for alkene formation, along with its utility in the preparation of phosphonium ylides for various synthetic processes, makes it an important compound in chemical synthesis and industrial applications. References 2014. Atom-economic threefold cross-couplings of triarylbismuth reagents with 2-halobenzaldehydes and pot-economic in situ Wittig functionalizations with phosphonium salts. RSC Advances, 4(104). DOI: 10.1039/C4RA13348J 2015. Triphenylphosphonium Cations of the Diterpenoid Isosteviol: Synthesis and Antimitotic Activity in a Sea Urchin Embryo Model. Journal of Natural Products, 78(6). DOI: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.5b00124 1980. Effects of phosphonium compounds on Schistosoma mansoni. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 23(8). DOI: 10.1021/jm00182a010 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Methyltriphenylphosphonium bromide |