Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Shanghai Daji Medical Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13816245196 | |||
 |
sales1@djpharm.com | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2019 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Classification | Chemical reagent >> Organic reagent >> Hydrazine |
|---|---|
| Name | N-(prop-2-en-1-yl)(tert-butoxy)carbohydrazide |
| Synonyms | tert-butyl N-amino-N-prop-2-enylcarbamate |
| Molecular Structure | 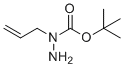 |
| Molecular Formula | C8H16N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 172.22 |
| CAS Registry Number | 21075-86-5 |
| EC Number | 881-789-6 |
| SMILES | CC(C)(C)OC(=O)N(CC=C)N |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 225.8±33.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)* |
| Flash point | 90.4±25.4 ºC (Calc.)* |
| Index of refraction | 1.474 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H312-H315-H319-H332-H335 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P264-P264+P265-P270-P271-P280-P301+P317-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P317-P319-P321-P330-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P403+P233-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
N-(prop-2-en-1-yl)(tert-butoxy)carbohydrazide is a functionalized hydrazide in which the nitrogen atom of the carbohydrazide is substituted with a prop-2-en-1-yl group and protected with a tert-butoxy (Boc) group. This compound belongs to the class of N-protected hydrazides, which are widely used in organic synthesis as intermediates for the construction of heterocycles, acyl hydrazones, and other functionalized derivatives. The combination of an alkene moiety and a Boc-protected hydrazide provides both reactivity and stability, allowing selective chemical transformations. The synthesis of N-(prop-2-en-1-yl)(tert-butoxy)carbohydrazide typically begins with the reaction of tert-butyl carbazate (Boc-hydrazine) with an allyl halide or allylic alcohol under conditions that promote N-alkylation. Protection of the hydrazide nitrogen with the Boc group prevents side reactions at the other nitrogen and allows selective introduction of the allyl substituent. The product is usually purified by recrystallization or column chromatography to yield a crystalline solid suitable for further synthetic applications. In organic synthesis, this compound serves as a versatile intermediate for the preparation of hydrazone derivatives, which can be used in condensation reactions with aldehydes or ketones to form functionalized imines. The allyl group provides a handle for further modifications, such as metathesis, epoxidation, or selective oxidation, while the Boc group can be removed under acidic conditions to reveal the free hydrazide for subsequent reactions. The dual functionality allows for stepwise construction of more complex molecules. In medicinal chemistry, derivatives of N-(prop-2-en-1-yl)(tert-butoxy)carbohydrazide can be explored as scaffolds for enzyme inhibitors, heterocyclic compounds, and other bioactive molecules. The hydrazide functionality is known to engage in hydrogen bonding and covalent interactions with biological targets, while the allyl group offers additional reactivity for derivatization. The Boc protection ensures stability during multi-step syntheses, enabling controlled functionalization of the hydrazide. The compound is also relevant in chemical methodology research, particularly for studying selective N-alkylation reactions, protective group strategies, and the reactivity of allylic hydrazides. Its combination of an alkene and a protected hydrazide allows chemists to investigate novel synthetic routes to nitrogen-containing heterocycles and functionalized intermediates for medicinal and material applications. Physically, N-(prop-2-en-1-yl)(tert-butoxy)carbohydrazide is generally obtained as a solid with moderate solubility in polar organic solvents such as dichloromethane, ethanol, and dimethylformamide. It is stable under standard laboratory conditions but should be protected from strong acids, bases, and oxidizing agents that may compromise the Boc group or the allyl functionality. Proper storage ensures its suitability for synthetic and research applications. Overall, N-(prop-2-en-1-yl)(tert-butoxy)carbohydrazide is a multifunctional N-protected hydrazide with an allyl substituent, combining stability and reactivity. Its chemical features make it a valuable intermediate for the synthesis of hydrazones, heterocycles, and bioactive molecules, as well as a useful tool in methodology development and organic synthesis. References 2009. Alkylation of Hydrazides. Science of Synthesis. URL: https://science-of-synthesis.thieme.com/app/text/?id=SD-040-00831 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for N-(prop-2-en-1-yl)(tert-butoxy)carbohydrazide |