Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Shanghai Worldyang Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13651600618 +86 (21) 5679-5779 | |||
 |
sales7777@worldyachem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: 13651600618 | |||
 |
WhatsApp: +86 13651600618 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink premium supplier since 2023 | ||||
| Hangzhou Verychem Science And Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8816-2785 +86 13606544505 | |||
 |
lucy@verychem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2004 | ||||
| chemBlink massive supplier since 2021 | ||||
| Classification | Biochemical >> Amino acids and their derivatives >> Other protected amino acids |
|---|---|
| Name | Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate |
| Synonyms | Di-tert-butyl pyrocarbonate; Dicarbonic acid bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)ester; Pyrocarbonic acid di-tert-butyl ester |
| Molecular Structure | 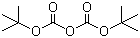 |
| Molecular Formula | C10H18O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 218.25 |
| CAS Registry Number | 24424-99-5 |
| EC Number | 246-240-1 |
| SMILES | CC(C)(C)OC(=O)OC(=O)OC(C)(C)C |
| Density | 0.949 |
|---|---|
| Melting point | 22-24 ºC |
| Boiling point | 56-57 ºC (0.5 torr) |
| Refractive index | 1.4075-1.4095 |
| Flash point | 37 ºC |
| Hazard Symbols |



 GHS02;GHS05;GHS06;GHS07 Danger Details
GHS02;GHS05;GHS06;GHS07 Danger Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H225-H226-H228-H315-H317-H318-H319-H330-H335 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P233-P240-P241-P242-P243-P260-P261-P264-P264+P265-P271-P272-P280-P284-P302+P352-P303+P361+P353-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P305+P354+P338-P316-P317-P319-P320-P321-P332+P317-P333+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P370+P378-P403+P233-P403+P235-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Di-tert-butyl carbonate, commonly known as Boc anhydride, is a compound that has been widely used in organic synthesis and medicinal chemistry since its discovery. First synthesized by Gross and Jones in 1959, the compound has proven to be of great value due to its unique properties and versatility in modifying organic molecules. Di-tert-butyl carbonate is a colorless crystalline solid with the molecular formula C₁₀H₁₈O₅. It is characterized by high stability and inertness under typical reaction conditions, which makes it an ideal reagent for protecting amino groups in organic synthesis. This ability stems from its ability to reversibly acylate amines to form Boc-protected amines that are widely used in peptide synthesis and other organic reactions. The discovery of di-tert-butyl carbonate revolutionized peptide chemistry, providing a method for selectively protecting amino groups (-NH₂) in amino acids and peptides. This protection prevents unwanted side reactions during peptide assembly, allowing chemists to accurately control the sequence and structure of peptides and proteins. This advance has played a key role in pharmaceutical research, enabling the synthesis of peptide-based drugs and biochemical probes with greater stability and specificity. In addition to peptide chemistry, di-tert-butyl dicarbonate can be used in a variety of organic transformations. It can be used as a carbonylating agent to introduce Boc groups by reacting with nucleophiles under mild conditions. This versatility extends its use to the synthesis of a variety of organic compounds, including pharmaceutical intermediates, agrochemicals, and materials science. In pharmaceuticals, Boc-protected intermediates are essential for the synthesis of complex molecules and natural products. The Boc group can be selectively removed under mild acidic conditions to expose the free amine without altering other functional groups, making it a preferred method in drug development and chemical biology. In addition, di-tert-butyl dicarbonate plays an important role in polymer chemistry, where its controllable reactivity and stability facilitate the synthesis of functionalized polymers and materials with tailored properties. The applications of di-tert-butyl dicarbonate continue to expand as researchers explore new synthetic methods and interdisciplinary applications. Its role in protecting groups, carbonylation reactions, and drug development highlights its importance in modern organic chemistry and pharmaceutical science. References 2024. Asymmetric dearomative single-atom skeletal editing of indoles and pyrroles. *Nature Chemistry*, 16(12). DOI: 10.1038/s41557-024-01680-0 2024. Open-vessel polymerization of N-carboxyanhydride (NCA) for polypeptide synthesis. *Nature Protocols*, 19(11). DOI: 10.1038/s41596-024-01062-3 1982. tert-Butoxycarbonylation of tyrosine and other phenolic amino acids with di-tert-butyl pyrocarbonate. *Chemistry of Natural Compounds*, 18(1). DOI: 10.1007/bf00581621 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate |