Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Yanuo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (311) 8363-7769 8363-7766 8365-9619 | |||
 |
info@yanuo.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1994 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2005 | ||||
| Simagchem Corporation | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13806087780 | |||
 |
sale@simagchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (551) 6541-8684 | |||
 |
sales@tnjchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2001 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Flowers Source Perfumery | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (512) 5746-2284 | |||
 |
sales@ks-bhy.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1994 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Langfang Hawk Techology & Development Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (316) 222-4727 | |||
 |
info@hawk-chinachem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1992 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| BOC Sciences | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 485-4226 | |||
 |
info@bocsci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Hangzhou Hairui Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8669-1155 | |||
 |
sales@hairuichem.com | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2005 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2017 | ||||
| Finetech Industry Limited | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (27) 8746-5837 +86 18971612321 | |||
 |
sales@finetechnology-ind.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2009 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2019 | ||||
| Classification | Flavors and spices >> Synthetic spice >> Carboxylic acid and ester perfume >> Aliphatic carboxylate |
|---|---|
| Name | Ethyl levulinate |
| Synonyms | Levulinic acid ethyl ester 4-oxopentanoate; 4-Oxopentanoic acid ethyl ester; Ethyl laevulinate; Ethyl Ethyl 4-oxovalerate; Ethyl 4-ketovalerate; Ethyl 3-acetylpropionate |
| Molecular Structure | 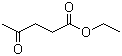 |
| Molecular Formula | C7H12O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 144.17 |
| CAS Registry Number | 539-88-8 |
| EC Number | 208-728-2 |
| FEMA | 2442 |
| SMILES | CCOC(=O)CCC(=O)C |
| Density | 1.012 |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 93-94 ºC (18 torr) |
| Refractive index | 1.421-1.423 |
| Flash point | 90 ºC |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H227-H302+H332-H319 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P305+P351+P338 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Ethyl levulinate is an important organic compound that has garnered attention in both the chemical and biofuel industries due to its versatile applications and renewable origin. It is an ester formed from levulinic acid and ethanol, with the molecular formula C8H14O3. The compound is known for its pleasant fruity aroma and has been classified as a flavoring agent in food products. The discovery of ethyl levulinate can be linked to the increasing interest in levulinic acid, which is derived from biomass through the acid hydrolysis of cellulose. The development of this compound began in the mid-20th century when researchers were exploring ways to convert lignocellulosic biomass into valuable chemicals. Ethyl levulinate can be synthesized through the esterification of levulinic acid with ethanol in the presence of an acid catalyst, making it an attractive candidate for green chemistry practices. One of the primary applications of ethyl levulinate is as a solvent and an intermediate in organic synthesis. The compound is used in the production of various pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and fine chemicals, demonstrating its utility as a building block in synthetic organic chemistry. Its relatively low toxicity and high biodegradability make it a suitable alternative to conventional organic solvents in many processes, aligning with the principles of sustainable chemistry. In addition to its role in organic synthesis, ethyl levulinate has emerged as a potential biofuel additive. The compound has been investigated for its properties as an oxygenated fuel, which can enhance the combustion efficiency of traditional fuels while reducing emissions of harmful pollutants. Ethyl levulinate exhibits a high cetane number, making it an appealing candidate for blending with diesel fuels. Its use as a biofuel can help mitigate the environmental impact of fossil fuels, contributing to a more sustainable energy landscape. The compound's flavoring properties have also been explored in the food and beverage industry. Ethyl levulinate is recognized for imparting fruity notes to various products, including baked goods, beverages, and confections. Its safety for consumption has been affirmed by regulatory agencies, which has facilitated its incorporation into food formulations. The pleasant aroma and flavor profile of ethyl levulinate enhance the sensory experience of consumers, making it a valuable additive in food processing. Research continues to explore new applications for ethyl levulinate, particularly in the context of green chemistry and sustainable practices. The compound is being studied for its potential in polymer production, where it can serve as a renewable monomer for creating bioplastics. Its properties as a biodegradable and renewable resource align well with the growing demand for environmentally friendly materials. In summary, ethyl levulinate is a compound of significant interest due to its diverse applications in organic synthesis, biofuels, and the food industry. Its renewable origins, favorable chemical properties, and low toxicity make it an attractive option in the pursuit of sustainable practices across multiple sectors. As research advances, ethyl levulinate may uncover further opportunities for use, contributing to innovations in green chemistry and the development of sustainable materials and products. References 2024. Dual-Acidity Catalysts for Alkyl Levulinate Synthesis from Biomass Carbohydrates: A Review. BioEnergy Research, 17(2). DOI: 10.1007/s12155-024-10726-7 2023. Sustainable Synthesis of A Novel Zirconium-Coordinated Biochar Catalyst from Sawdusts for Conversion of Ethyl Levulinate to γ-Valerolactone. Catalysis Letters, 153(9). DOI: 10.1007/s10562-023-04440-w 1982. New phosphonic analogs of aspartic and glutamic acid by aminoalkylation of trivalent phosphorus chlorides with ethyl acetyloacetate or ethyl levulinate and benzyl carbamate. Monatshefte für Chemie - Chemical Monthly, 113(1). DOI: 10.1007/bf00814338 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Ethyl levulinate |