Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Simagchem Corporation | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13806087780 | |||
 |
sale@simagchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| Shenzhen BrightChina Industrial Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (755) 2603-1978 2603-1979 | |||
 |
bright@brightcn.net | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (551) 6541-8684 | |||
 |
sales@tnjchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2001 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Zhengzhou Yi Bang Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (371) 6677-7261 | |||
 |
paulinecao2010@zzyibang.cn | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| BOC Sciences | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 485-4226 | |||
 |
info@bocsci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| BLIT (Hefei) Chemical Co.,ltd | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86-551-62622640 | |||
 |
info@blitchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2017 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2024 | ||||
| Aronis | Russia | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+7 (926) 578-0336 | |||
 |
rakishev@aronis.ru | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| Anvia Chemicals, LLC | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (414) 534-7845 | |||
 |
sales@anviachem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| Classification | Flavors and spices >> Synthetic spice >> Carboxylic acid and ester perfume >> Aliphatic carboxylate |
|---|---|
| Name | Ethyl L(-)-lactate |
| Synonyms | (S)-(-)-2-Hydroxypropionic acid ethyl ester |
| Molecular Structure | 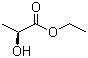 |
| Molecular Formula | C5H10O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 118.13 |
| CAS Registry Number | 687-47-8 |
| EC Number | 211-694-1 |
| FEMA | 2440 |
| SMILES | CCOC(=O)[C@H](C)O |
| Density | 1.034 |
|---|---|
| Melting point | -26 ºC |
| Boiling point | 154 ºC |
| Refractive index | 1.42-1.414 |
| Flash point | 46 ºC |
| alpha | -10 º (neat) |
| Water solubility | SOLUBLE |
| Hazard Symbols |


 GHS02;GHS05;GHS07 Danger Details
GHS02;GHS05;GHS07 Danger Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H226-H318-H335 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P233-P240-P241-P242-P243-P261-P264+P265-P271-P280-P303+P361+P353-P304+P340-P305+P354+P338-P317-P319-P370+P378-P403+P233-P403+P235-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transport Information | UN 1192 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Ethyl L(-)-lactate is an ester derived from lactic acid, which is a natural byproduct of the fermentation process. Its chemical structure consists of ethyl and lactic acid moieties, forming a compound with unique properties that distinguish it from other substances in its class. The L(-)-enantiomeric configuration ensures that it meets specific purity and regulatory standards, enhancing its suitability for a variety of applications. The outstanding feature of ethyl L(-)-lactate is its environmentally friendly nature. As a derivative of lactic acid, it can be obtained from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugar cane, which supports sustainable practices in chemical manufacturing. In addition, its biodegradability and non-toxic properties make it a preferred choice as a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional chemicals. In the pharmaceutical industry, ethyl L(-)-lactate plays a variety of roles. It serves as a solvent for active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), ensuring the stability and effectiveness of the formulation. Its biocompatibility and low toxicity make it suitable for drug delivery systems and topical applications, contributing to the advancement of medicine and healthcare. Ethyl L(-)-lactate can be used for food flavoring and preservation. As a flavoring agent, it imparts a mild fruity flavor and aroma to foods, enhancing their sensory appeal. Additionally, its antimicrobial properties help extend the shelf life of perishable goods, in line with consumer demand for safer, longer-lasting food options. In industrial settings, ethyl L(-)-lactate is used as a solvent in coatings, paints, and cleaning formulations. It is able to dissolve a wide range of substances, and due to its low volatility and mild odor, it is ideal for applications that require controlled evaporation rates and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional solvents. Looking ahead, ongoing research and development efforts are exploring new uses for ethyl L(-)-lactate and improving its existing applications. Advances in biotechnology and materials science are expected to unlock further potential, potentially expanding its role in renewable energy storage, biodegradable plastics, and more. References 2016. The Asymmetric Reduction of Acetophenone and Its Derivatives to (S)-Aromatic Secondary Alcohols by Rhodotorula mucilaginosa CCTCC M2014255 Resting Cells. Catalysis Letters, 146(5). DOI: 10.1007/s10562-016-1730-9 2015. Self-assembly of coil-rod-coil triblock copolymers depending on lateral methyl groups at the interface of rod and coil segments. Macromolecular Research, 23(10). DOI: 10.1007/s13233-015-3122-1 2013. Toward more environmentally friendly routes to high purity ionic liquids. MRS Bulletin, 38(7). DOI: 10.1557/mrs.2013.155 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Ethyl L(-)-lactate |