Formamidine hydrochloride is an organic salt derived from formamidine and hydrochloric acid, consisting of the protonated formamidine cation and a chloride anion. This compound is a crystalline solid, highly soluble in water, and is widely used as an intermediate in organic synthesis, particularly in the preparation of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and heterocyclic compounds. Its utility stems from the nucleophilic character of the nitrogen atoms in the formamidine moiety, which allows formation of a variety of substituted amidines and heterocycles.
The discovery of formamidine hydrochloride is linked to early research into amidine chemistry in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, when chemists investigated the properties of nitrogen-containing functional groups and their salts. Formamidine itself is a simple compound with a highly reactive imine structure, and its hydrochloride salt was found to be more stable and easier to handle than the free base, making it suitable for synthetic applications.
In organic synthesis, formamidine hydrochloride is used as a key building block for the preparation of guanidine derivatives, amidines, and heterocyclic scaffolds such as pyrimidines and triazines. Its reactivity with carbonyl compounds, alkyl halides, and other electrophiles allows the formation of carbon-nitrogen bonds under mild conditions. This makes it a versatile reagent in pharmaceutical chemistry for constructing biologically active molecules, including antiviral, antibacterial, and anticancer agents.
The compound is also employed in the synthesis of pesticides and insecticides. Many formamidine derivatives have been developed as selective acaricides, targeting mites and ticks in agricultural and veterinary applications. Formamidine hydrochloride serves as a precursor for these active compounds, facilitating chemical modification to tune selectivity, stability, and bioactivity. Its solubility and reactivity allow straightforward conversion into complex derivatives that exhibit desired pharmacological or pesticidal effects.
Formamidine hydrochloride is typically prepared by treating formamidine free base with hydrochloric acid in an aqueous or alcoholic medium. The reaction results in the formation of the crystalline hydrochloride salt, which can be filtered, washed, and dried. The crystalline form improves stability and handling safety, making it suitable for industrial-scale applications. The product is usually characterized by melting point, solubility, and spectral data to confirm purity and identity.
In addition to its synthetic applications, formamidine hydrochloride is occasionally used as a reagent in laboratory studies to explore nitrogen-centered reactivity, including condensation reactions and formation of coordination complexes with metals. Its basicity and nucleophilicity provide a convenient platform for examining reactions that involve iminium or amidine intermediates.
Overall, formamidine hydrochloride is a versatile and stable intermediate in organic chemistry. Its role as a building block for heterocyclic compounds, pharmaceuticals, and agrochemicals underscores its importance in both research and industrial applications. The combination of water solubility, chemical reactivity, and crystalline stability makes formamidine hydrochloride a practical and widely used reagent in modern chemical synthesis.
|













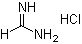
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details