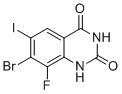
7-Bromo-8-fluoro-6-iodoquinazoline-2,4(1H,3H)-dione is a halogenated heterocyclic compound derived from the quinazoline-2,4-dione core structure. This molecule features a bicyclic aromatic system composed of a fused benzene and pyrimidine ring, with carbonyl groups at the 2- and 4-positions and halogen atoms substituted at the 6-, 7-, and 8-positions. The specific substitution pattern includes iodine at position 6, bromine at position 7, and fluorine at position 8 on the benzene ring of the quinazoline scaffold.
Quinazoline-2,4-dione compounds are well known in medicinal chemistry due to their presence in bioactive molecules and their structural similarity to purine bases found in DNA and RNA. The incorporation of halogen atoms into this core structure imparts distinct electronic and steric properties, influencing both reactivity and potential biological activity. Fluorine, due to its electronegativity and size, modulates electronic density and can enhance metabolic stability. Bromine and iodine, being larger and more polarizable, are excellent leaving groups and allow for further derivatization through metal-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions.
The synthetic preparation of 7-bromo-8-fluoro-6-iodoquinazoline-2,4(1H,3H)-dione typically involves stepwise halogenation of a quinazoline-2,4-dione precursor. Electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions are employed under controlled conditions to introduce each halogen selectively. The order of halogenation and the directing effects of existing substituents are critical in achieving the desired substitution pattern without affecting the integrity of the heterocyclic ring.
This compound's densely functionalized structure makes it a valuable intermediate in synthetic chemistry. Its halogen atoms provide reactive sites for palladium-catalyzed transformations such as Suzuki–Miyaura, Sonogashira, or Buchwald–Hartwig couplings, enabling the installation of a wide range of functional groups. These reactions facilitate the design of structurally complex molecules with potential pharmaceutical or agrochemical applications.
In pharmaceutical development, quinazoline derivatives bearing halogens have been explored as kinase inhibitors, antimicrobial agents, and anticancer candidates. Although specific bioactivity for this particular derivative may not be extensively documented, its structural features make it a promising scaffold for drug discovery efforts. The electron-deficient nature of the quinazoline ring, combined with the presence of two carbonyl groups and strategically placed halogens, enhances its utility as a core structure for rational design of small-molecule modulators.
In conclusion, 7-bromo-8-fluoro-6-iodoquinazoline-2,4(1H,3H)-dione is a chemically versatile heterocycle. It offers multiple sites for chemical modification through its halogen substituents and serves as a platform for the synthesis of complex heterocyclic compounds with potential applications in medicinal and synthetic organic chemistry.
|



 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details